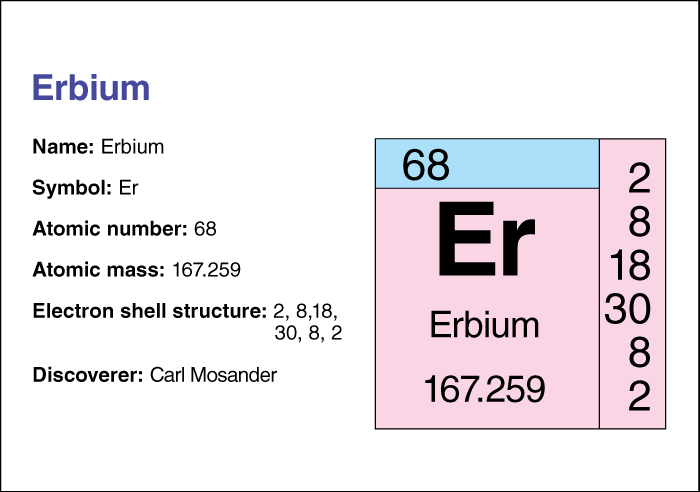
Erbium << UR bee uhm >> (chemical symbol, Er) is one of the lanthanide metals. Its atomic number (number of protons in its nucleus) is 68. It has a relative atomic mass of 167.259. An element’s relative atomic mass equals its mass (amount of matter) divided by 1/12 of the mass of carbon 12, the most abundant form of carbon. For information on the position of erbium on the periodic table, see the article Periodic table.
Erbium has six known relatively stable isotopes, atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Erbium is found associated with the heavier lanthanides, such as europium and gadolinium, chiefly in the yttrium minerals. Erbium of high purity is available commercially. The metal has a grayish-silver color. It melts at 1529 °C and boils at 2868 °C. It has a density of 9.066 grams per cubic centimeter at 25 °C.
Erbium forms a rose-pink oxide used to make pink glass. Erbium is also used in laser technology and is added to certain alloys (metal mixtures) to improve hardness.
The Swedish scientist Carl Mosander discovered it in 1843.
See also Rare earth; Yttrium.
