Fermi, << FUR mee or FEHR mee, >> National Accelerator Laboratory is a high-energy physics laboratory in Batavia, Illinois. Scientists from all over the world go to the laboratory to study subatomic particles. The laboratory is commonly called Fermilab.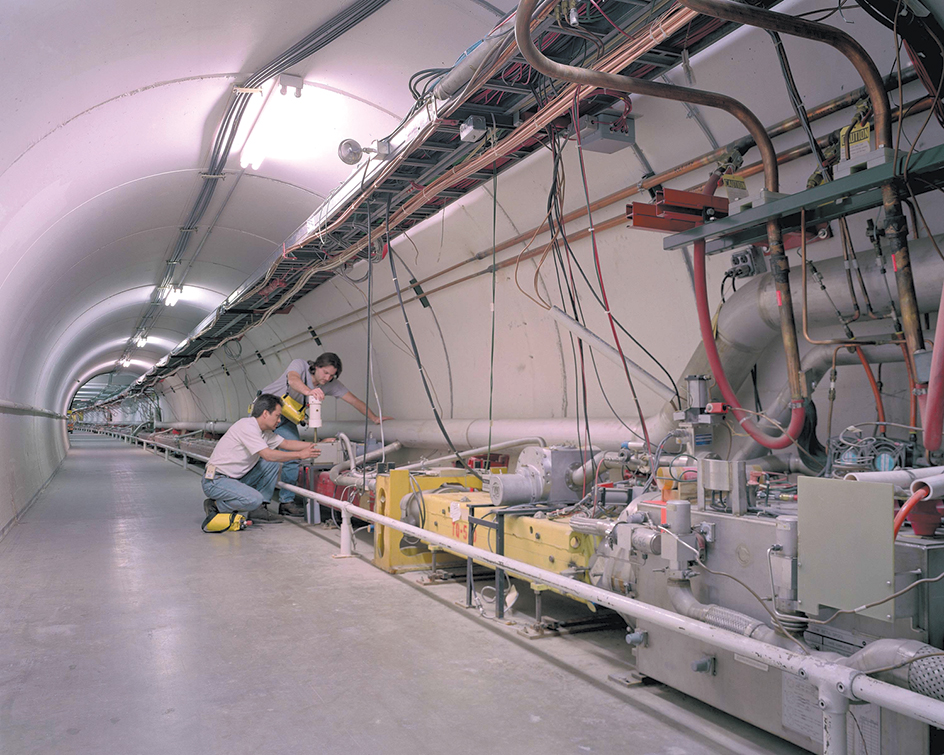 
Fermilab scientists study data collected by telescopes, observatories, and particle accelerators around the world. The Tevatron, a type of particle accelerator called a synchrotron, was the laboratory’s main instrument from 1972 to 2011. After the Tevatron shut down, scientists at Fermilab began using data collected by the more powerful Large Hadron Collider (LHC), outside Geneva, Switzerland. A type of particle called a neutrino is created and studied at Fermilab using special particle accelerators much smaller than the Tevatron or LHC.
The laboratory’s name honors Italian-born American physicist Enrico Fermi, the first person to produce a nuclear chain reaction. Fermi Research Alliance, LLC, a corporation owned by the University of Chicago and Universities Research Association, Inc.—a group of universities in the United States, Canada, Italy, and Japan—manages the laboratory. The Department of Energy pays for the operation of it.