Goose is a water bird that resembles the duck and swan. Like ducks and swans, geese have a flattened bill; a long neck; water-repellent feathers; long, pointed wings; a short tail; short legs; and webbed feet. But geese are larger than ducks and smaller than swans, and they honk rather than quack or whistle. Male geese are called ganders.
Their webbed feet make geese good swimmers, but they are as much at home on land as in the water. All geese are migratory birds. Geese from the Northern Hemisphere fly south in the fall and north in spring. Geese from the Southern Hemisphere fly north in the fall and south in spring. Some species (kinds) of geese can fly more than 1,000 miles (1,600 kilometers) without stopping to rest.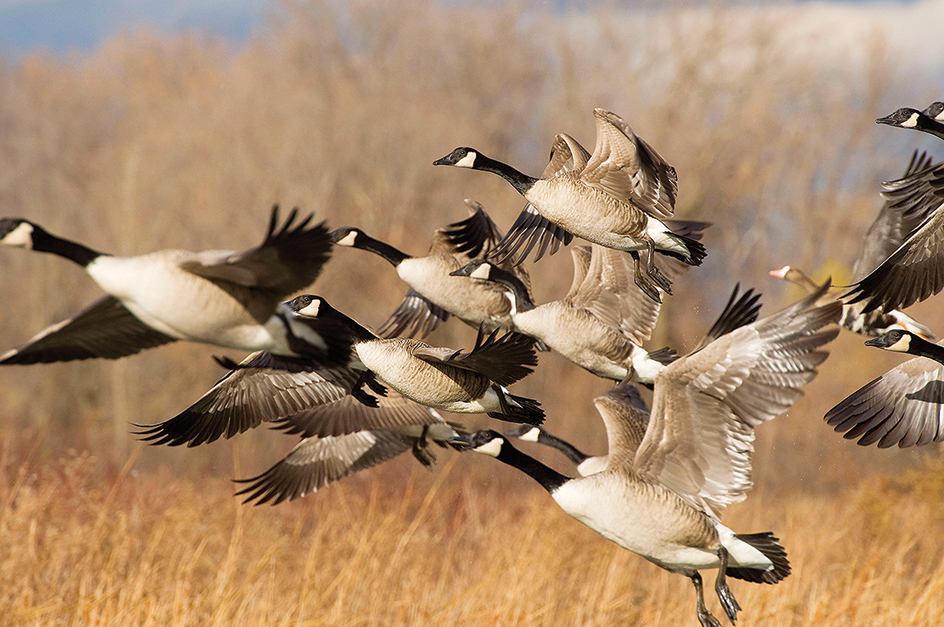 
There are numerous species of wild geese, found chiefly in Asia, Europe, and North America. Domestic geese are probably descended from two wild species—the graylag goose and the swan goose. Geese were first domesticated in Asia thousands of years ago. People raise geese for their rich, tasty meat and for their down (soft feathers). Goose down is widely used as stuffing in pillows and mattresses and as a lightweight, insulating material in sleeping bags and outdoor clothing.
The body of a goose.
Adult geese range in weight from about 31/4 pounds to 83/4 pounds (1.5 kilograms to 4.0 kilograms). Feathers cover most of the body of a goose, except for the legs and feet. The largest feathers are the long, stiff flight feathers of the wings and tail. The goose has a thick coat of down underneath its outer feathers. Scales cover the goose’s legs. The four clawed toes on each foot are connected by flaps of skin.
The goose has eyes on the sides of its head, and must turn its head to see objects in front of it clearly. The inner surface of the goose’s bill is sensitive, enabling the goose to find its food by touch as well as sight. Geese have a long esophagus (tube leading to the stomach), but the rest of their internal organs are similar to those of other birds. The uropygial gland, at the base of the tail, produces an oily substance the goose uses to preen (smooth) and waterproof its feathers.
Kinds of geese.
The Canada goose is one of the most common wild geese of North America. It has a grayish-brown body with whitish underparts and a black head, bill, and neck. A white band stretches across its throat and cheeks. During the summer, Canada geese nest from Alaska and northern Canada to the northern half of the United States. They spend the winter as far south as northern Florida and northern Mexico.
The graylag goose has grayish-brown feathers, an orange bill, and pink legs and feet. It nests in Iceland and throughout northern Europe and northern Asia. Its wintering grounds stretch across southern Europe and southern Asia. The swan goose has its nesting grounds in northeastern Asia. Its winter range extends south to Korea, Japan, and China. The swan goose is brown, with a black bill and orange legs. Other wild geese include the snow goose and the saltwater brant.

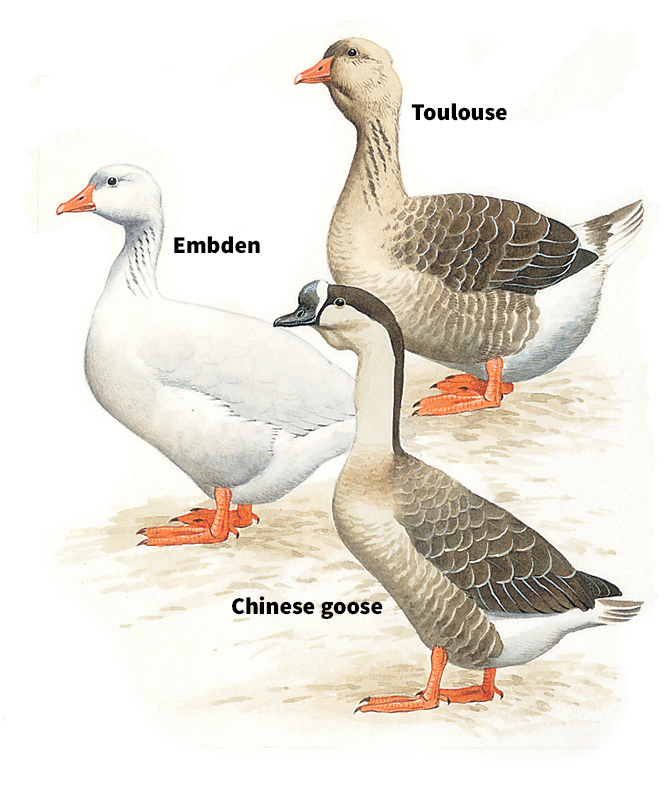
Breeders have developed many varieties of domestic geese. The Embden is a graceful white goose with a rounded breast. The Toulouse is a stocky gray bird. It has a flap of skin, called a dewlap, that hangs beneath its jaw. The Chinese goose and the African goose both have a large knob on the bill. Other domestic geese include the Sebastopol and the American buff.
The life of a wild goose.
Wild geese feed chiefly on water plants, grasses, corn, and wheat. During fall migrations, they may hunt for food in cropland stubble. Migrating geese fly in large groups, often in a V-shaped formation. Some naturalists believe geese use this formation because air currents created by the birds in front make flying easier for the rest of the birds. Others believe that the V-shaped formation enables the geese to follow one leader, helping them to stay together.
Loading the player...Flock of domestic geese
Geese arrive at their northern nesting grounds in early spring. Young adult geese select mates at this time, and will stay with the same mate for life. The mating pair chooses a nesting site on the ground, away from the rest of the flock. The female then fashions a nest from twigs, grass, weeds, and moss, and lines the nest with down. The female may lay several eggs, not more than one a day. She stays on the nest almost continuously, frequently turning the eggs with her bill. While the female tends the eggs, the male defends the site.
The eggs generally hatch in 28 to 32 days. The goslings (young geese) are covered with fine, fluffy down. They can hunt for food as soon as they hatch but must be protected from the cold for at least the first few days. Goslings learn to swim a few days after hatching. They grow rapidly during the summer and develop sturdy feathers for flying. They begin to fly after about two months. Young geese stay with their parents for at least a year. As fall approaches, the adult geese shed their feathers and grow a new set. The geese gather into large groups to feed and fatten themselves in preparation for the migration to warmer wintering grounds.
Geese have many natural enemies, including foxes, wolves, and coyotes. Small mammals and gulls and other sea birds may steal goose eggs and attack goslings. Geese defend themselves by hissing and biting, and by striking with their wings. They have long lives and sometimes reach over 30 years of age in captivity.
Raising geese.
Goose farming is common in Europe and Asia. Many geese are also raised on large farms in Canada and the United States. Most geese are raised outdoors in pens or in fenced fields where they can graze. Goose farmers use special poultry feed to promote rapid growth. The feed consists of such ingredients as corn or another grain, soybean meal, meat by-products, vitamins, and minerals. Geese are slaughtered for meat when they are several months old. Foie gras, a traditional French delicacy, is made from fatty goose livers. The livers are enlarged by forcing the geese to eat more food than they ordinarily would. Many countries have outlawed this feeding practice.
See also Bird; Brant; Canada goose; Feather; Swan.
