Gymnastics is a competitive sport for both men and women in which participants demonstrate body control over a wide range of acrobatic exercises and other movements. Gymnasts must develop balance, endurance, flexibility, and strength. Gymnastics may also be a recreational or educational activity.

Two or more teams compete in a gymnastics meet. The gymnasts use equipment called apparatus and a variety of mats. Judges evaluate each gymnast’s performance, called a routine, for its difficulty, skill, and technical precision. Judges then assign a score to the performance. The most common form of competitive gymnastics is artistic gymnastics.
Friedrich Jahn, a German schoolteacher, built the first modern gymnastics equipment in the early 1800’s. The sport has been a part of the Olympic Games since the modern Olympics began in 1896. Worldwide television coverage has helped gymnastics grow in popularity as a spectator sport.
Men’s events
A men’s artistic gymnastics meet consists of six events. These events, in order of performance, are the (1) floor exercise, (2) pommel horse, (3) still rings, (4) vault, (5) parallel bars, and (6) horizontal bar. Men who compete in all six events are called all-around gymnasts. Those who enter fewer than six events are called specialists.
Loading the player...Men's floor exercise
The floor exercise
is performed on a mat that measures approximately 40 feet (12 meters) square. The gymnast should use the entire mat area during the exercise, which consists primarily of tumbling movements in different directions. The floor exercise must not take longer than 70 seconds.
The pommel horse
is named for the padded piece of apparatus on which this event is held. The horse measures about 46 inches (1.15 meters) high, about 14 inches (35 centimeters) wide, and about 5 feet 3 inches (1.6 meters) long. It has two handles on top called pommels. The hands are the only part of the body that should touch the horse. Pommel horse routines consist of continuous circular movements interrupted only by required scissors movements with the legs.
Loading the player...Pommel horse
The still rings
event is performed on two rings suspended from cables about 9 feet (2.75 meters) above the floor. The athlete supports his body in various strength hold positions, which require exceptional upper body strength and control. In a movement called the iron cross, for example, the athlete supports himself in an upright position with his arms extended sideways. At least one position of strength must be held for two seconds during the routine. It is essential that the gymnast remain motionless and maintain proper body position while performing strength elements.
Loading the player...Still rings
The vault
is performed on a piece of apparatus called a vault table. The table is about 4 feet (1.25 meters) high, 37 inches (95 centimeters) wide, and about 37 to 41 inches (95 to 105 centimeters) long. The gymnast approaches the table at a fast run and jumps onto a springboard. He then springs off the board and places both hands on the vault table for support as he goes over it. He may perform any of several movements while in the air, such as a twist or a somersault.
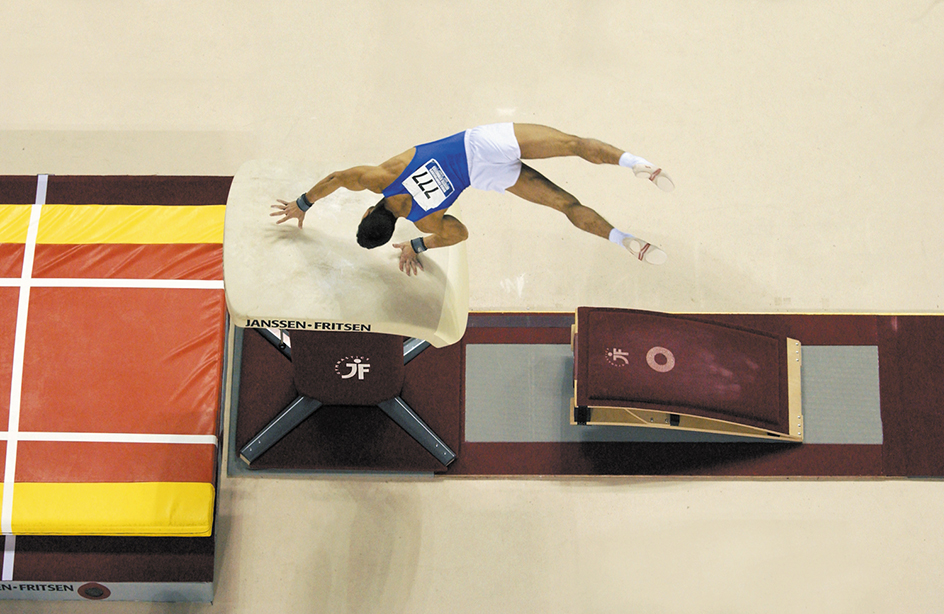
The parallel bars
is an event performed on two long and slightly flexible bars about 6 feet 6 inches (1.95 meters) above the floor and about 16.5 to 20.5 inches (42 to 52 centimeters) apart. The athlete supports himself on the bars with his hands while performing handstands, swings, twists, and other required movements. This event requires a great deal of hand-eye coordination, timing, and balance.
Loading the player...Parallel bars
The horizontal bar
event takes place on a somewhat flexible bar fastened about 9 feet (2.75 meters) above the floor between two supports. During the routine, the gymnast must execute a series of continuous swings and turns and at least one move in which he releases and regrasps the bar. The routine ends with a landing called a dismount, which often includes multiple somersaults and twists before hitting the floor.
All-around competition
for men consists of all six events. The gymnast performs in each event, selecting his own routine within required categories.
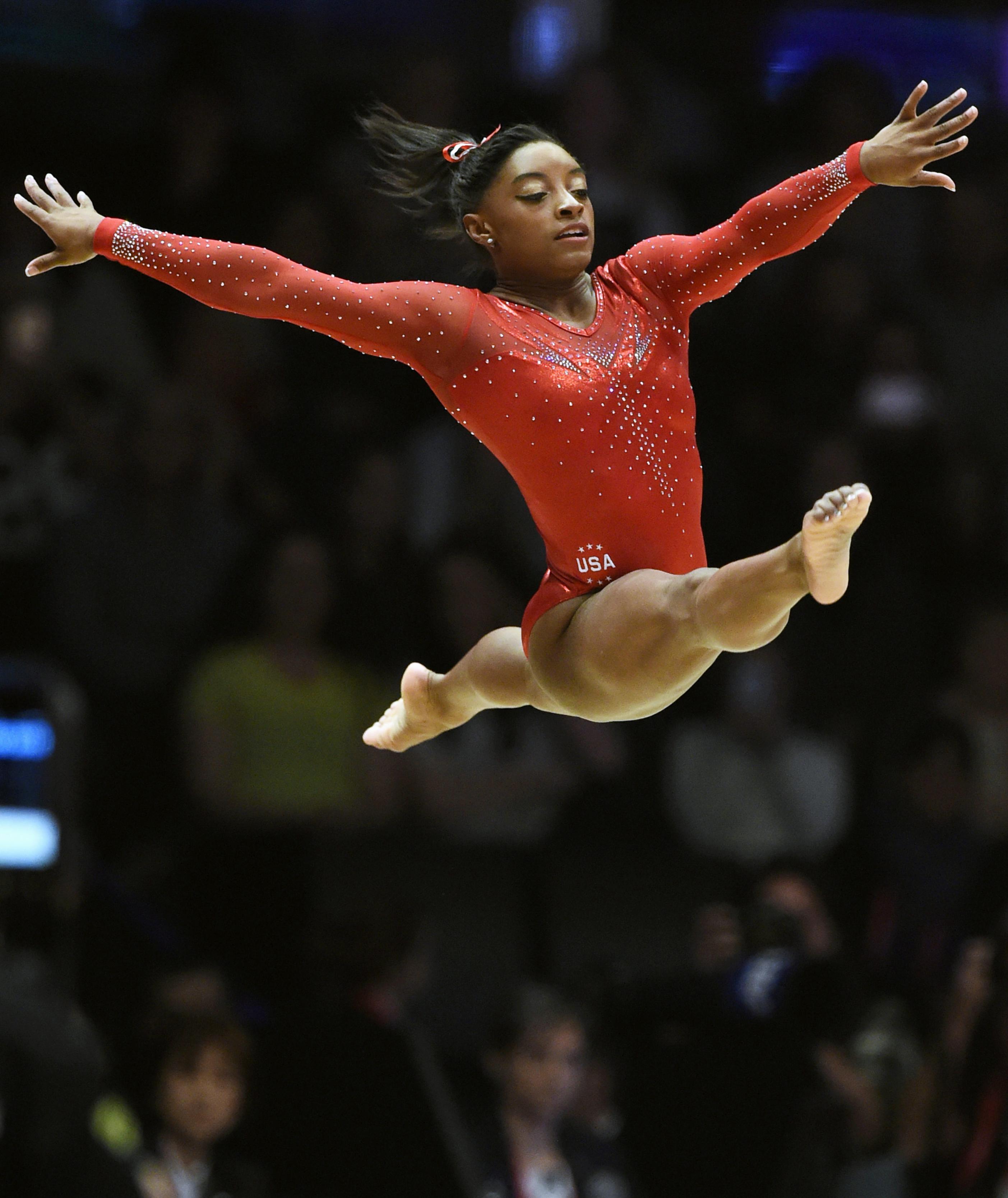
Women’s events
A women’s artistic gymnastics meet consists of four events. In order of performance, they are the (1) vault, (2) uneven bars, (3) balance beam, and (4) floor exercise. Most women gymnasts enter all four events.
Loading the player...Uneven bars
The vault
is performed in the same general manner as the men’s vault. The apparatus is also the same.
The uneven bars
is an event performed on two parallel bars. The higher bar’s height is about 8 feet (2.46 meters), and the lower bar is about 5 feet 6 inches (1.66 meters) high. The gymnast swings around one bar at a time, performing maneuvers requiring great flexibility and agility. She switches rapidly back and forth from one bar to another, trying to keep in constant motion.
The balance beam
event is performed on a beam about 16 feet (5 meters) long, 4 inches (10 centimeters) wide, and about 4 feet (1.25 meters) above the floor. Gymnasts perform jumps, leaps, acrobatic movements, and turns and must use the beam’s full length. The routine must not exceed 90 seconds.
Loading the player...Balance beam
The floor exercise
is performed to music on a mat approximately 40 feet (12 meters) square. The event allows gymnasts to express their personality through their choice of music and choreography (dance movements). The routine must last no longer than 90 seconds and cover the entire floor space. Certain acrobatic movements and dance elements are required.
Loading the player...Women's floor exercise
All-around competition
for women includes all four events. Each gymnast performs in each event, selecting her own routine.
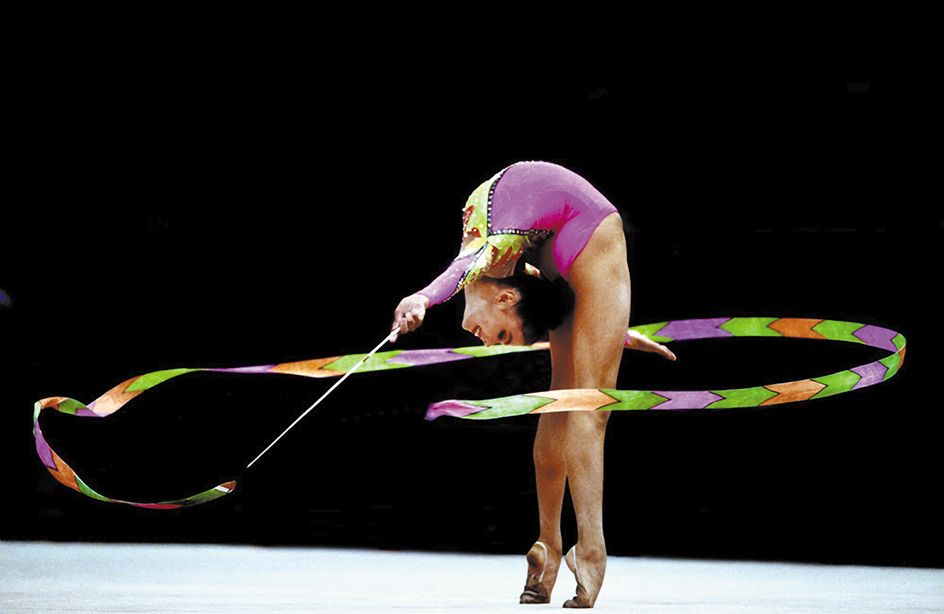
Rhythmic gymnastics
Rhythmic gymnastics is a separate type of gymnastics competition for women. It involves body movements and dance combined with the handling of small apparatus—a rope, a hoop, a ball, clubs, or a long ribbon. Routines must cover the entire mat and include jumps, leaps, balances, and flexibility movements.
Loading the player...Rhythmic gymnastics
Rhythmic gymnasts perform as individuals or in a group on a carpet about 43 feet (13 meters) square. The group event involves five gymnasts who perform simultaneously. Each group must perform two routines. One of the routines is performed with pieces of apparatus that are identical. The other routine is choreographed with mixed equipment. The time limit for individual routines is 75 to 90 seconds. The time limit for groups is 2 minutes 15 seconds to 2 minutes 30 seconds.
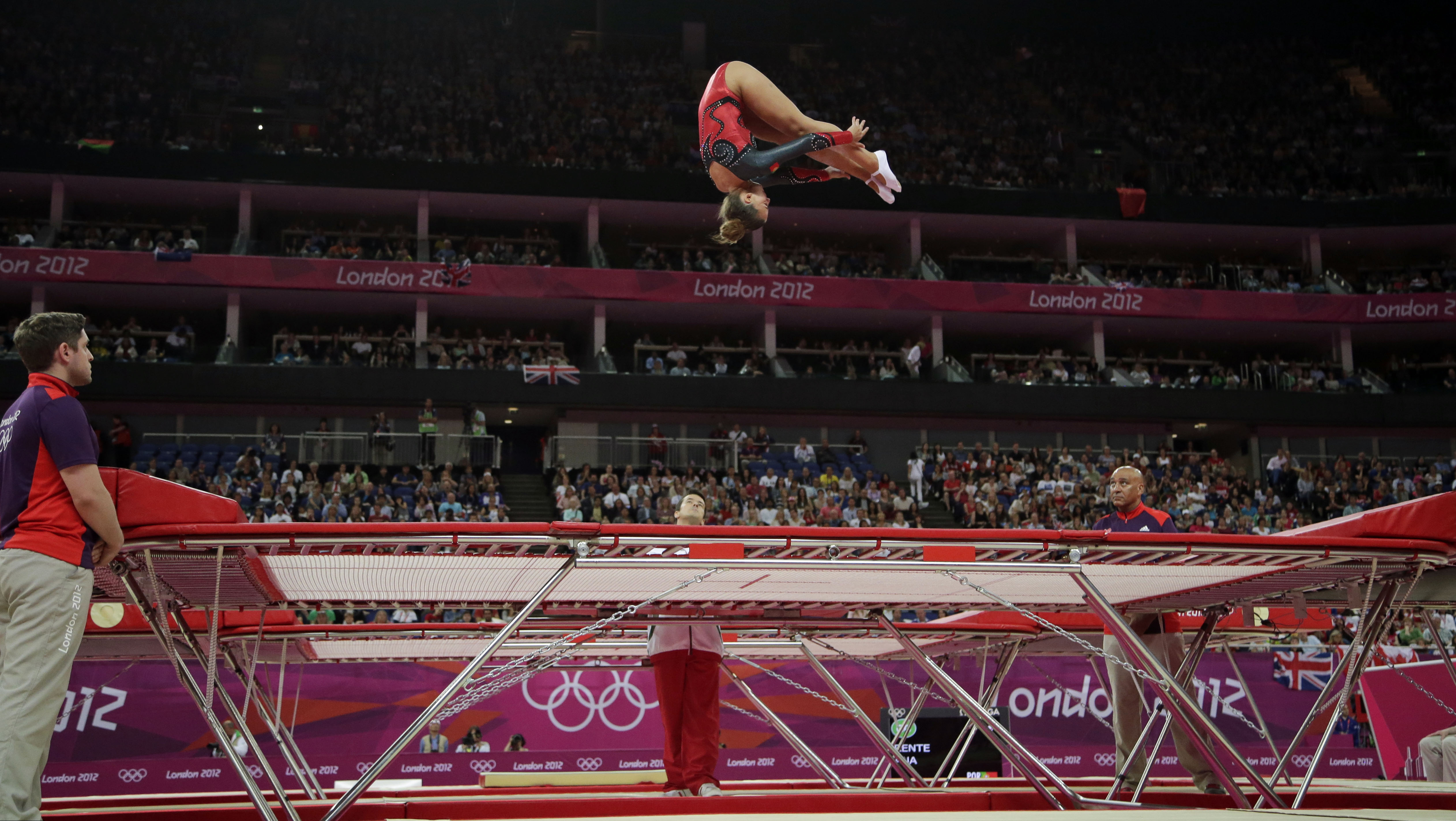
Trampoline and tumbling
Trampoline
routines are performed on a woven-web string bed 7 by 14 feet (about 2.1 by 4.3 meters) in size that can propel the gymnast up to 30 feet (about 9 meters) in the air. At the Olympic Games level, competition consists of three routines, each of which covers 10 skills. In the first routine, the skills to be performed are specified. In the second and third routines, the athlete selects the skills. At the age-group and developmental level, the requirements of routines vary. In synchronized trampoline, two athletes using two trampolines perform identical 10-skill routines at the same time. The total score includes a performance (execution) score, a difficulty rating, and a synchronization score.

Power tumbling
is performed on a platform 6 by 88 feet (about 1.8 by 27 meters) in size. Tumblers demonstrate speed, strength, and skill while executing a series of acrobatic maneuvers. Athletes perform two 8-skill routines in both the preliminary round and the final round. In the preliminary round, the first pass focuses on somersaulting. The second pass requires athletes to show their twisting skills. In the final round, athletes complete routines of their own choosing.
Double mini-trampoline
involves a small, narrow trampoline with an angled mounting area and a level dismount area. The event combines the running speed of tumbling and the aerial skills of trampoline. Competitors perform two 2-skill routines of their own choosing in preliminaries and two 2-skill routines in the finals. A good routine shows height, multiple flips and twists, and a dismount with no extra steps before coming to a stop.
Acrobatic gymnastics
Acrobatic gymnastics (formerly known as sports acrobatics) consists of five events that are performed on a mat similar to the one gymnasts use for floor exercises. The acrobatic events are (1) women’s pair, (2) men’s pair, (3) mixed pair, (4) women’s trio, and (5) men’s four. Smaller and more flexible athletes perform in the top, or “flyer,” positions. Taller and stronger athletes take the lower positions. Each pair or group performs routines that feature gymnastics tumbling skills, balances, and dynamic skills. Balance routines consist of such elements as pyramids and handstands. Dynamic routines involve somersaults and twists with landings on the floor or catches by a partner.
Gymnastics competition
Judging.
At the highest level of gymnastics competition, four to nine judges sit at each piece of apparatus. Each routine receives a score for difficulty and a score for execution. The two scores are combined to create the final score. The difficulty score begins at 0.0 and increases with every difficult skill performed. The execution score begins at 10.0, and the judges deduct for errors in performance. There is no limit to how high a gymnast may score. However, the top performances typically receive scores in the middle to high 15’s. A score of 16 is considered exceptional. In rhythmic gymnastics, a score may reach a maximum of 20 points. The athlete is scored on execution and difficulty. The combination of these two scores creates the final score.

In trampoline competition, two difficulty judges give the difficulty score for each routine, starting with 0 points. A panel of five judges assesses the execution of each routine, giving a score up to 10. Execution is weighted more heavily than difficulty. The two scores, plus a time of flight score, are combined for the final result. The time of flight element was introduced to trampoline competition in 2011. An electronic device with a laser sensor is fastened to the frame of a trampoline. The sensor measures the length of time an athlete spends in the air—that is, the length of time between foot strikes on the trampoline bed. The longer the flight time, the higher the score.
Acrobatic gymnastics competitions are decided on a score that can reach 30 points or more. A maximum score of 10 is allotted to an artistic component and another maximum of 10, to an execution component. A difficulty component can be a maximum of 10 in junior competition but greater than 10 in senior competition. The three individual scores are combined to create the final score.
Organization.
The International Gymnastics Federation, which is based in Lausanne, Switzerland, governs international gymnastics. The federation is known by its French acronym, FIG (for Fédération Internationale de Gymnastique).
National federations, such as Gymnastics Australia in Australia, British Gymnastics in the United Kingdom, and USA Gymnastics in the United States, supervise the sport in most countries. The national federations conduct programs for men and women in all of the disciplines of gymnastics. These programs determine the members of each nation’s teams for international competition. Such competition includes the Olympic Games; continental championships such as the Pan American Games, the European Championships, and the Asian Games; the Commonwealth Games; and the World Championships, the World Games, and the World University Games.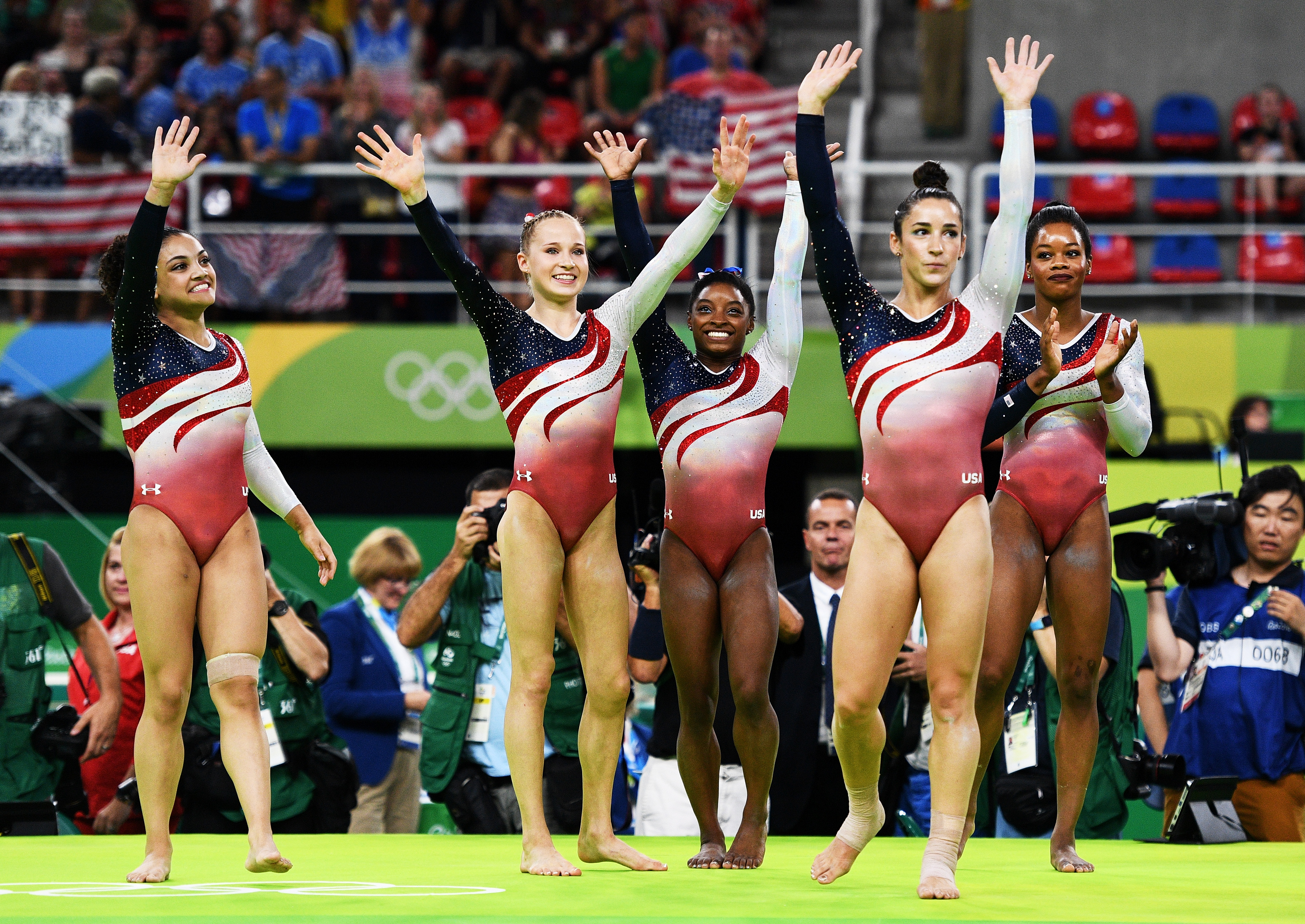 
In the United States, many states hold a championship competition for high school and Junior Olympic athletes. The competition may qualify athletes for regional competition, national competition, or both. The National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) has men’s and women’s championships. USA Gymnastics holds men’s and women’s USA Gymnastics Collegiate Championships.
