Holistic, << hoh LIHS tihk, >> medicine, also spelled wholistic medicine, is an approach to health care based on the observation that many factors affect a person’s health. Such factors include genetics, nutrition, physical activity, stress, family relationships, medical care, living and working conditions, and the environment. But any single factor might be the most important one for a particular person. The term holistic medicine comes from the Greek word holos, meaning whole.
Loading the player...Holistic medicine
The emphasis of holistic medicine differs from that of traditional medicine. Traditional medicine focuses chiefly on the treatment of disease. Holistic medicine emphasizes the prevention and treatment of disease. In addition, some of its methods of diagnosis and treatment are not usually used in traditional medical practice. For example, physicians who practice holistic medicine use many treatments in addition to drugs and surgery. These methods include acupuncture, herbs, homeopathy, hypnosis, and relaxation therapies. Holistic physicians try to reduce the excessive use of drugs.
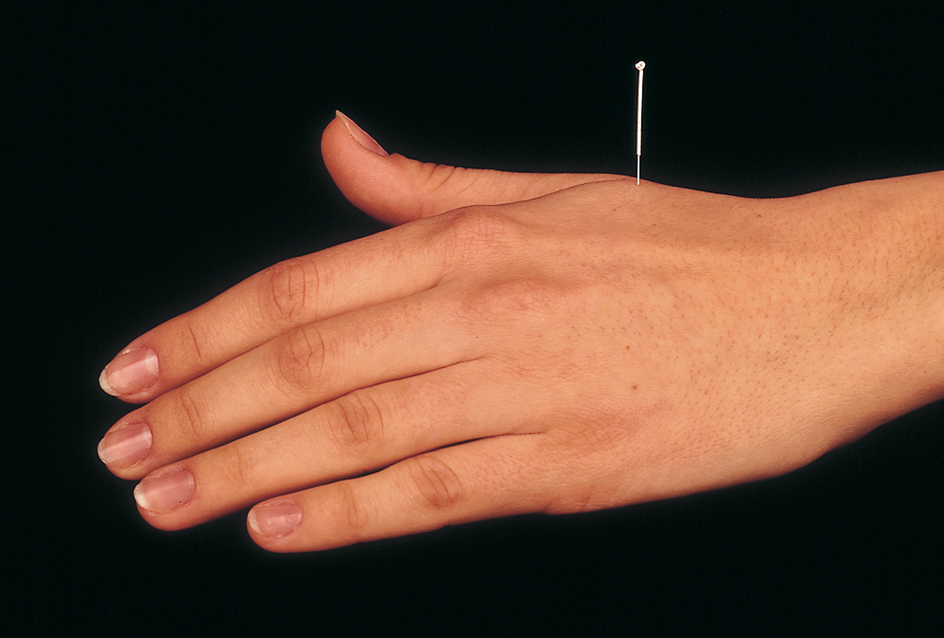
Many physicians, psychologists, and other health care professionals practice holistic medicine. Holistic practitioners stress the responsibility of the patient in achieving and maintaining the best possible health. They help patients establish good health habits, and they emphasize the importance of a physical environment that is free of toxic exposure. They also may teach patients various methods of medical self-care. For example, a patient might learn to control a normally involuntary body process, such as the rate of the heartbeat, by means of relaxation techniques, meditation, or biofeedback (see Biofeedback ).
The idea of a holistic approach to health is as old as medicine itself. Good medical practice has always included elements of holistic medicine. After the early 1970’s, holistic medicine gained increasing popularity in many countries. Its popularity grew because many people realized that the most common noninfectious diseases, including cancer and heart disease, were related to specific life styles and personal habits, such as smoking and diet.
