Hotbed is a low, heated enclosure in which plants are grown during cold weather. Gardeners use hotbeds in spring to sprout seeds before the growing season. Hotbeds also protect plants from cold in fall and winter.
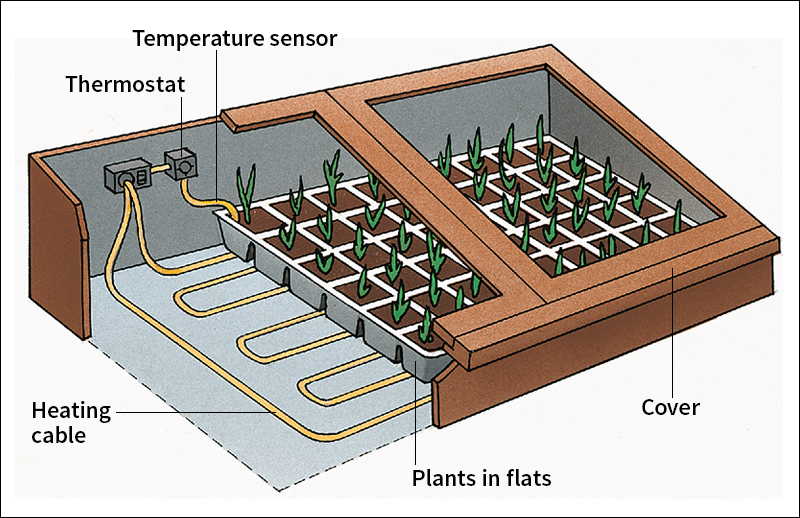
A hotbed consists of a four-sided wood or concrete frame built on the ground and covered by glass or transparent plastic. The cover is slanted to allow the maximum amount of sunlight to enter and help warm the growing area. Most of the warmth comes from electric heating cables, which are located under the soil and controlled by thermostats. In large hotbeds, such as those used by professional gardeners, the heat comes from pipes that surround the growing area or are buried in the soil. A furnace sends steam, hot water, or hot air through the pipes to heat the frame.
Gardeners once heated hotbeds by burying a thick layer of manure under the soil. As the manure decayed, it produced heat and fertilized the soil. A structure similar to a hotbed but heated only by sunlight is called a cold frame (see Cold frame ).
