Judah is the name of a region occupied by one of the Twelve Tribes of Israel in the Hebrew Bible . The Bible describes a region west of the Dead Sea in the land of Canaan (later called Palestine ). The name Judah comes from the Hebrew name Yehudah. The size and boundaries of Judah varied during different periods throughout history. 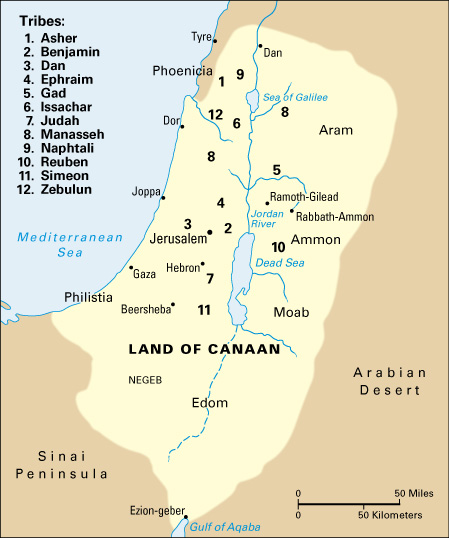
The early Jewish people , called the Hebrews or Israelites, were organized into 12 tribes descended from the sons of Jacob (also called Israel), an early ancestor of the Jews. One of the tribes was descended from Jacob’s son Judah and lived in the region called Judah. About 1025 B.C., the Israelites chose a king named Saul to lead them. David , from the tribe of Judah, succeeded Saul as king and unified the Israelites to form the kingdom of Israel. He established a capital at Jerusalem . David’s son Solomon followed him as king. The reign of David, and later Solomon, is known as the United Monarchy.
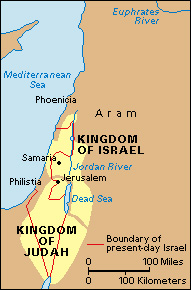
The kingdom of Judah was ruled by David’s descendants until the Babylonians conquered it in 587 or 586 B.C. Some Israelites were forced into exile in Babylonia. The Persians conquered Babylonia in 539 B.C., and the emperor Cyrus the Great allowed the exiled Israelites to return to Judah. During Persian rule, the area also was known as Yehud, the Aramaic form of Judah.
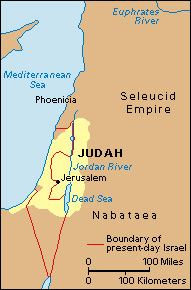
Judea came under Roman control in 63 B.C., and its size was reduced. It became a client kingdom (dependent state) of the Roman Republic, then a province of the Roman Empire. The Jews revolted against Roman rule in A.D. 66. The Romans destroyed the Jewish Temple in Jerusalem in 70 and defeated the revolt in 73. The Romans defeated a second Jewish revolt, led by Simeon Bar Kokhba, in 135. The Roman Emperor Hadrian then rebuilt Jerusalem, renamed the city Aelia Capitolina, and banned the Jews from it. Hadrian adopted the name Palestine for the region.
