Leo is a constellation known as the Lion. It sits between the constellations Cancer and Virgo in the night sky. It is best viewed around March through May. The sun passes through Leo from around mid-August through mid-September. Leo was among the 48 constellations defined by the ancient Greek mathematician Ptolemy. Today, it is one of 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union, the leading authority in the naming of heavenly objects. Leo is also one of the 12 signs of the zodiac used in astrology (see Leo).
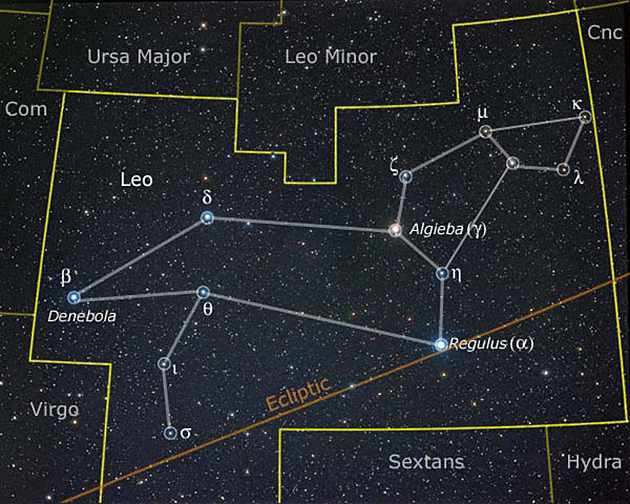
Leo can be drawn in several ways using a different number of stars. One helpful approach includes 13 main stars. Four stars define the lion’s head. A pentagon of stars forms its neck and mane. The remaining stars mark out a rectangular body with two legs and a tail. Drawings that use a smaller number of stars typically leave out the legs and use fewer stars for the head, neck, and mane.
The Leonids are a well-known meteor shower that appears to originate in Leo. They occur every year around November 17. Peaks in the number of meteors occur with a period of about 33 years. So, an exceptional Leonid meteor shower that occurred in 1999 will be repeated in 2032 (see Leonids).
