Mango is a fruit that grows in tropical regions throughout the world. It serves as the main food of many people in tropical countries and is often called the king of tropical fruits. Mangoes are eaten fresh or are used in making desserts, preserves, and some other foods. The fruit is an excellent source of vitamins A and C.
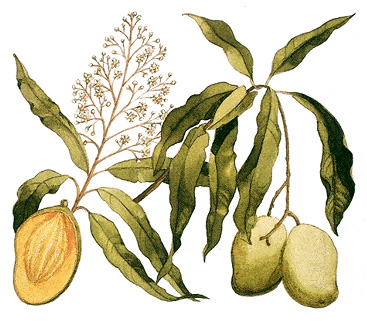
Most mangoes are kidney-shaped, oval, or round. They vary from about 2 to 10 inches (5 to 25 centimeters) in length and from 2 ounces to 5 pounds (57 grams to 2.3 kilograms) in weight. Mangoes have a smooth, leathery skin that surrounds a juicy, yellow or orange pulp and a hard inner pit. The skin may be green, purple, or various shades of orange, red, or yellow. Many mangoes have tough fibers in their pulp, and some of the fruits have an unpleasant turpentinelike odor. However, mangoes grown commercially have a soft, fiberless pulp and a sweet, spicy taste and odor.
The mango tree is an evergreen that grows about 70 feet (21 meters) tall. It has long, slender leaves and small, pinkish-white flowers. The fruit develops from the ovaries of the blossoms and ripens about five months after the flowers bloom.
Mangoes were first cultivated about 4,000 years ago in India and the Malay Archipelago. In the 1700’s and 1800’s, European explorers brought mangoes from India to other tropical countries. Today, farmers grow mangoes in Brazil, India, Mexico, and the Philippines. In the United States, mangoes grow in Florida and in Hawaii.
