Midnight sun is a term used for the sun when it can be seen 24 hours a day in Earth’s polar regions. At the North Pole, the sun never sets for six months, from about March 20 to September 23. At the South Pole, the sun remains above the horizon from about September 23 to March 20. The length of periods of continuous sunlight decreases as the distance from either pole increases. At an imaginary line called the Arctic Circle, such a period occurs for only a few days around June 21. At another imaginary line, the Antarctic Circle, it lasts for a day or two around December 21.
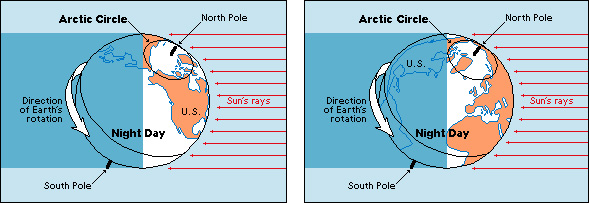
The midnight sun is caused by the tilting of Earth’s axis in one direction as Earth travels around the sun. One pole slants toward the sun for six months, while the other pole slants away from the sun and receives no sunlight. As Earth revolves around the sun, it also spins on its axis. This spinning motion makes the sun appear to rise and set at regular intervals, causing day and night on most of Earth.
