Nickel is a white metallic chemical element used in alloys. Its chemical symbol is Ni. Nickel is magnetic, takes a high polish, and does not tarnish easily or rust.
Nickel can be hammered into thin sheets or drawn into wires. One pound (0.4 kilogram) of pure nickel could be drawn into a wire 80 miles (130 kilometers) long. The Chinese used an alloy of nickel more than 2,000 years ago. Pure nickel was first isolated in 1751 by the Swedish scientist Axel Cronstedt.
Nickel has an atomic number (number of protons in its nucleus) of 28. Its relative atomic mass is 58.6934. An element’s relative atomic mass equals its mass (amount of matter) divided by 1/12 of the mass of carbon 12, the most abundant form of carbon. Nickel melts at 1455 °C and has a density of 8.908 grams per cubic centimeter at room temperature (see Density).
Chemists classify nickel as a transition metal. For information on the position of nickel on the periodic table, see the article Periodic table.
Industrial uses.
Nickel is used in structural work and in electroplating chiefly because it resists corrosion. Publishers often have printing plates electroplated with nickel to enable them to withstand hard use (see Electroplating). Nickel plays an important role in several types of batteries (see Battery).
An important use for nickel is to promote certain chemical reactions by catalysis (see Catalysis). The nickel itself is not changed in the process and can be used repeatedly. Nickel is used as a catalyst in a process called hydrogenation. The nickel causes some organic compounds to combine with hydrogen to form new compounds. Hydrogenation produces solid vegetable oils for cooking. See Hydrogenation.
Nickel-iron alloys.
Perhaps the largest use for nickel is as an additive to cast iron and steel. It makes iron more ductile (easily formed) and increases its resistance to corrosion. Nickel also makes steel more resistant to impact. Manufacturers often use steel alloyed with nickel to make armor plate and machine parts.
Invar
is an alloy of nickel, iron, and other metals. It is valued for meter scales and for pendulum rods. Invar expands or contracts very little as its temperature changes.
Monel metal
is an alloy of nickel and copper used in sheet-metal work. It has an especially high resistance to corrosion. See Monel metal.
Nickel silver,
also called German silver, is a nickel alloy used in tableware. See Nickel silver.
Mining nickel.
The chief mineral ore of nickel is pentlandite, a mixture of sulfur, iron, and nickel. Other nickel ores include millerite and niccolite.
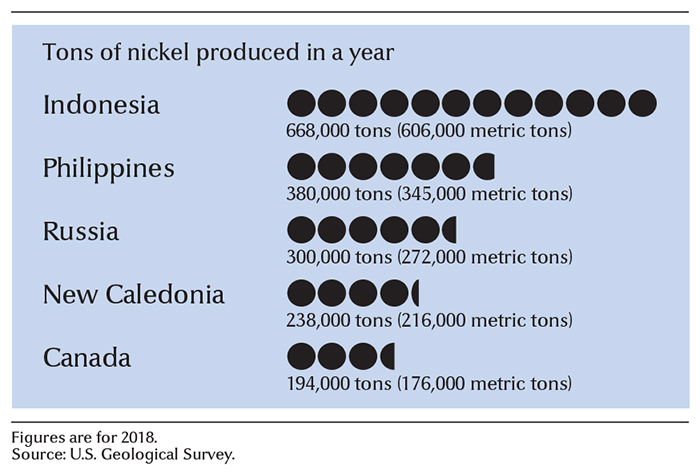
Indonesia, the Philippines, and Russia are the leading nickel producers. They combine to produce about half of the world total. Australia, Canada, and New Caledonia are also important nickel-producing areas.
