Oslo is the capital of Norway. The municipality of Oslo has a population of 673,469. A municipality may include rural areas as well as the urban center. Oslo is Norway’s chief economic, industrial, and cultural center, and one of its leading seaports. It lies on the southeast coast at the head of the great Oslo Fiord. The city is about 80 miles (130 kilometers) north of the Skagerrak, an arm of the North Sea. From 1624 until 1925, Oslo was called Christiania in honor of King Christian IV, who planned the rebuilding of the city after a fire destroyed it.
The Oslo metropolitan area covers about 175 square miles (454 square kilometers). But over two-thirds of the metropolitan area consists of forests and lakes. These features make the city a favorite recreation center.
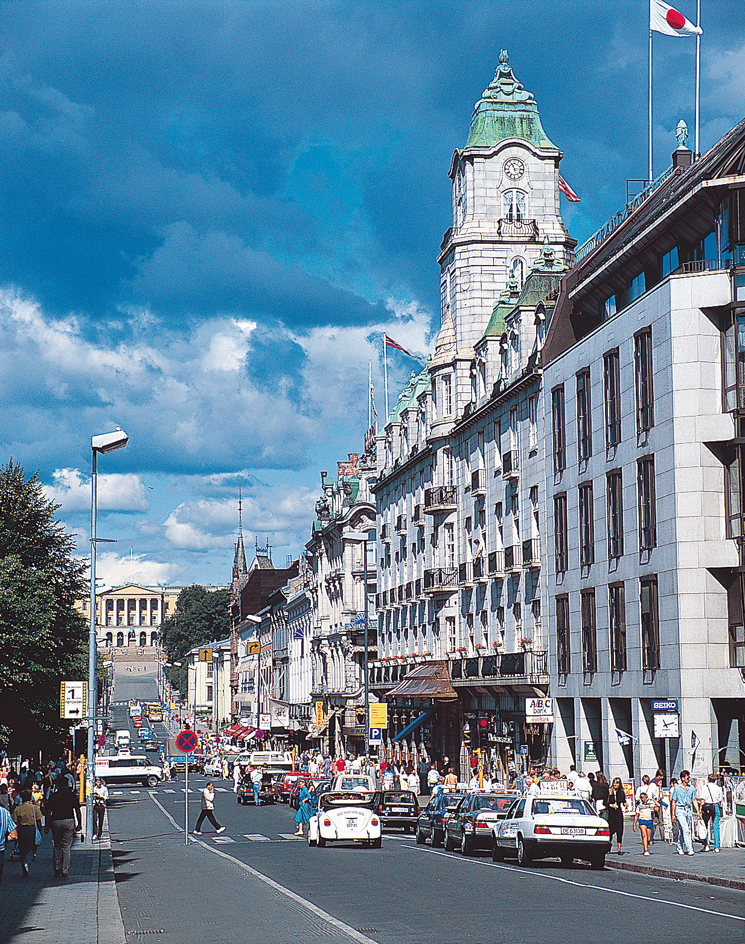

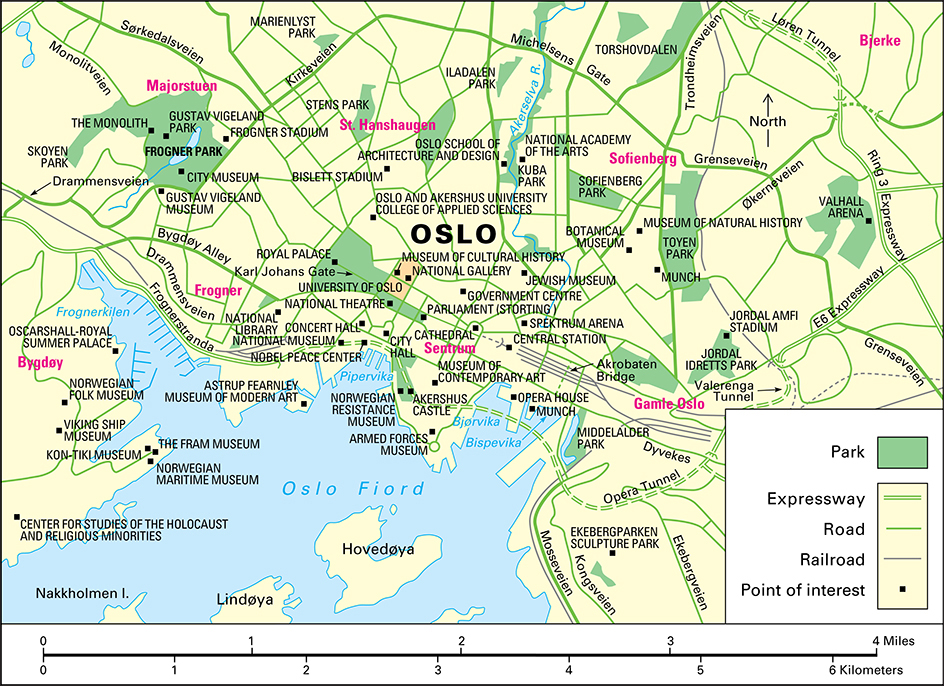
The Royal Palace and the Parliament Building stand along Karl Johans Gate, the main street in the central section of Oslo. City Hall, the medieval Akershus Castle, and the city’s commercial district are south of Karl Johans Gate. Most of Oslo’s people live in apartment buildings. The majority of Oslo’s single-family homes are located in outlying areas of the city.
Oslo has Norway’s oldest and largest university, an Evangelical Lutheran cathedral, and many museums. The Viking Ship Museum displays ships used by the Vikings about a thousand years ago. The Fram and Kon-Tiki museums house the Fram, a famous polar exploration ship; and the Kon-Tiki, the raft of anthropologist and adventurer Thor Heyerdahl (see Heyerdahl, Thor). Other museums include the National Museum, Norwegian Folk Museum, Norwegian Maritime Museum, and Historical Museum. Munch—a museum that contains the art of Edvard Munch—stands on the waterfront in the Bjørvika neighborhood. About 150 works by Gustav Vigeland, one of Norway’s greatest sculptors, are in Oslo’s Frogner Park.
Manufacturing employs about 25 percent of Oslo’s workers. Major industries include shipbuilding and the production of chemicals, machinery, metals, paper, textiles, and wood products. Banking, communications, electronics, food processing, shipping, and tourism also play important roles in the city’s economy. Oslo is the hub of the Norwegian national railroad system. An international airport lies just outside the city.
Oslo was founded by King Harold Hardrade about 1050. In 1299, Akershus Castle was built on a rocky peninsula overlooking the fiord. Fire destroyed Oslo in 1624, but the people rebuilt the city northeast of the castle. Norway was united with Denmark from 1380 to 1814, and with Sweden from 1814 to 1905. In 1905, it became independent, with Oslo as the capital. By the mid-1800’s, the city had grown into a major administrative, economic, and military center. The development of shipping and industry, plus the forest and agricultural resources of southeastern Norway, soon helped give Oslo the dominant role in the nation’s economy that it still has today.
