Siphon, << SY fuhn, >> is a device used to draw liquid over the edge of a container and transfer it to a lower level. Most siphons are a tube bent into the shape of an inverted U or J. Siphons have many uses. For example, siphons are used in plumbing and irrigation systems.
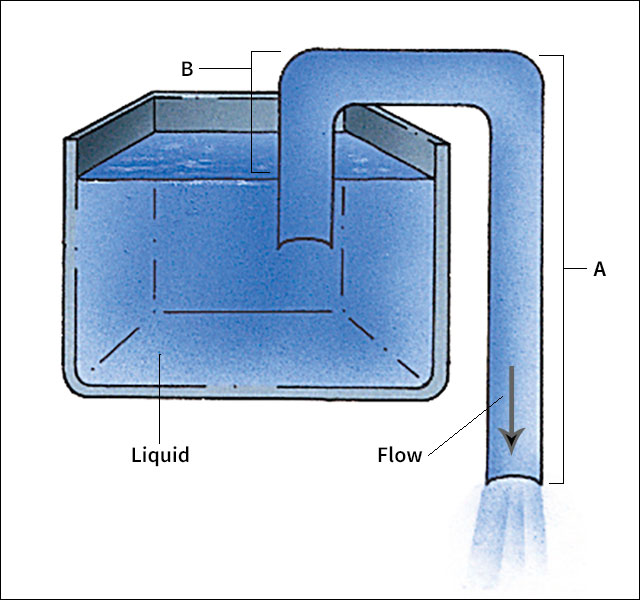
To operate a siphon, first put one end of the tube into a container of liquid. Next, place the other end at a level lower than the surface of the liquid. Then, apply suction to the lower end to fill the tube. When you release the suction, liquid will continue to flow upward into the tube and down and out the lower end.
In some siphons, the liquid flows out into a second container, whose liquid level is lower than that of the first container. Siphoning action continues until the liquid in both containers reaches the same level.
A siphon works because of gravity and liquid cohesion, the attraction between molecules in a substance. As shown in the accompanying illustration, the part of the siphon labeled A contains more liquid than does the part labeled B. The liquid in both parts are pulled downward by gravity. For all the liquid to fall, however, liquid at the top of the siphon would have to break apart. Cohesion between the liquid’s molecules hold the liquid together. The larger amount of liquid in part A is heavier than the liquid in part B, so only the liquid in part A falls. As it falls, it pulls liquid in part B through the tube, and it pulls liquid in the container up into the tube.
