Squash, also called squash rackets or squash racquets, is a fast indoor game similar to handball and racquetball. Squash is played with rackets (or racquets) and a hollow rubber ball about the size of a golf ball. The ball is either hard or soft, depending on the version of the game being played. Players use the rackets to hit the ball against the four walls of a court. A variety of shots is possible, and the ball travels at great speed. Two players play singles. Two teams of two players each play doubles.
There are two forms of squash—American, or hard ball, and English, or soft ball. The soft ball form is also called international. Since the early 1990’s, most players in North America as well as the rest of the world have adopted the soft ball form. A soft ball court is wider than a hard ball court. Many courts in the United States are hard ball courts, but a majority of people still play soft ball on them. Some matches are played on converted racquetball courts. This article discusses soft ball squash.
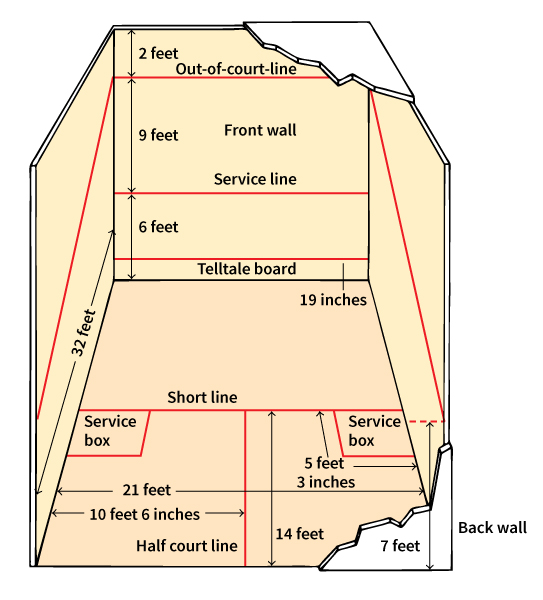
A soft ball squash court is 21 feet (6.40 meters) wide and 32 feet (9.75 meters) long. The out-of-court line, above which the ball is out-of-bounds, is 15 feet (4.57 meters) high on the front wall. The line slants down the side walls to 7 feet (2.15 meters) on the back wall. Doubles squash is played on a larger court. The surface of most squash courts is plaster, wood, or glass.
A player can only win a point while serving to the opponent, called the receiver. The player loses the serve in several ways, such as striking the ball more than once or serving onto or below a metal board called the telltale board or tin. The telltale board is 19 inches (48 centimeters) high at the bottom of the front wall. Generally, a player must score 9 points to win the game. But if a game is tied 8 to 8, the receiver may choose to continue to 9 points (known as set one) or continue to 10 points (known as set two). The first person to win three games wins the match.
Squash originated at Harrow School in England about 1850. The game was introduced into the United States about 1880.
