Strontium << STRON shee uhm >> a chemical element, is a soft, silvery metal. It exists as a number of isotopes, forms of the element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Strontium 90 is a dangerous radioactive isotope found in the fallout from some nuclear explosions. The isotope’s radioactivity destroys the tissues that produce blood in people and animals.
Strontium is found in the minerals celestite and strontianite. It combines readily with oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen. Strontium nitrate burns with a crimson flame, and is used in flares and fireworks.
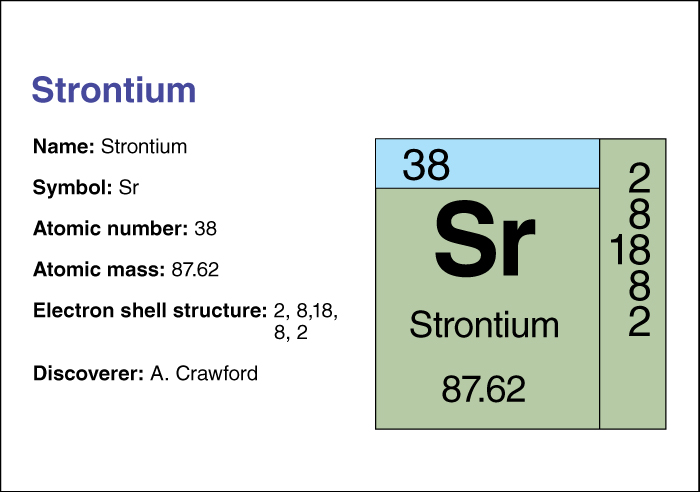
Strontium has the chemical symbol Sr. Its atomic number (number of protons) is 38. Its relative atomic mass is 87.62. An element’s relative atomic mass equals its mass (amount of matter) divided by 1/12 of the mass of carbon 12, the most abundant isotope of carbon. Strontium melts at 769 °C and boils at 1384 °C. Strontium belongs to a group of elements called the alkaline earth metals. For information on the position of strontium on the periodic table, see the article Periodic table.
Strontium was discovered in 1790 by Adair Crawford of Ireland.
