Terbium, << TUR bee uhm >> (chemical symbol, Tb), is a chemical element and one of the lanthanide metals. Terbium resembles silver in appearance. Many terbium compounds glow with a green color and are used in phosphors, dots on television picture tubes.
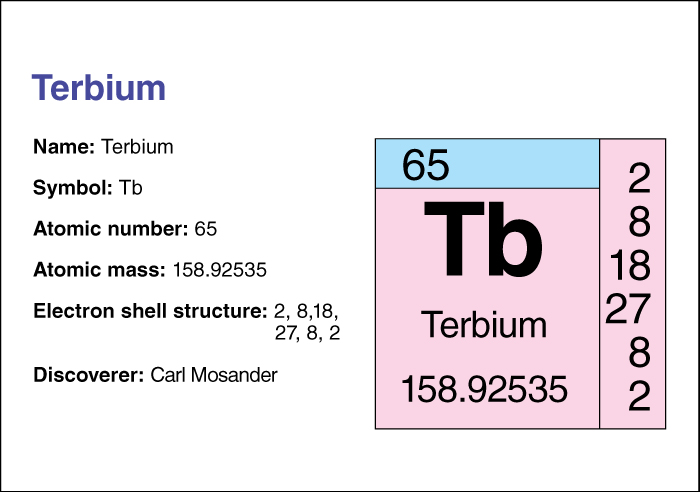
Terbium’s atomic number (number of protons in its nucleus) is 65. Its relative atomic mass is 158.92534. A chemical element’s relative atomic mass equals its mass (amount of matter) divided by 1/12 of the mass of carbon 12, the most abundant form of carbon. For information on the position of terbium on the periodic table, see the article Periodic table .
Terbium has a density of 8.23 grams per cubic centimeter at 24 °C. It melts at about 1356 °C and boils at around 3230 °C.
The Swedish chemist Carl Mosander first discovered terbium in 1843. Another chemist, Georges Urbain of France, first isolated it in an almost pure form in 1905.
See also Rare earth .
