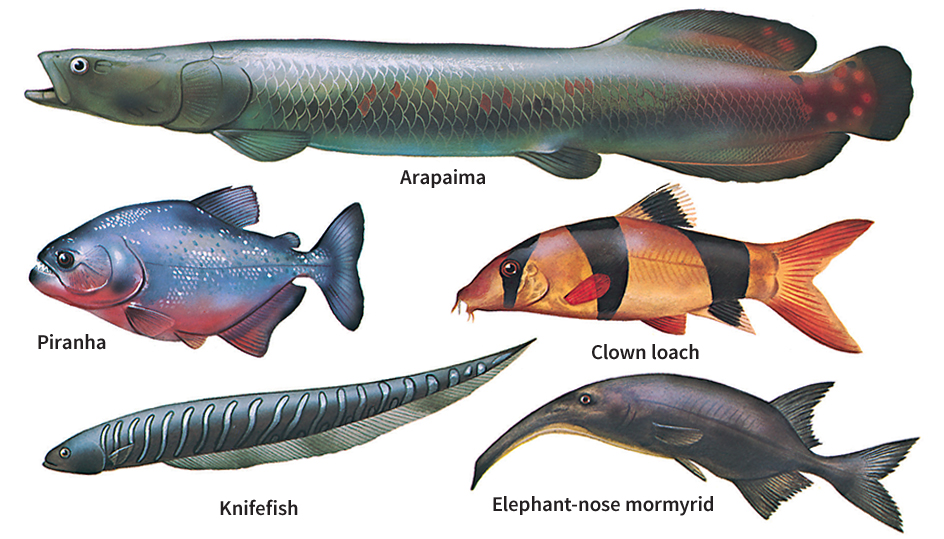
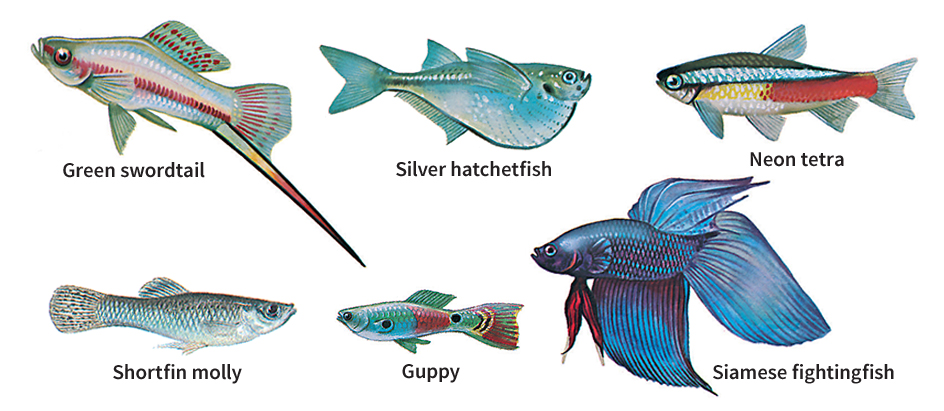
Tropical fish is a term normally applied to small, brightly colored fish from tropical habitats that are popular for home aquariums. Such fish breed rapidly and usually range in size from 1 to 12 inches (2.5 to 30 centimeters) long. Many other kinds of fish live in the tropics. However, this article will discuss some of the most common types bred for home aquariums.
Most tropical aquarium fish will eat food made from grains, dried shrimp, fish, insects, and aquatic plants. Such food can be bought in a pet shop. Small pieces of shrimp, oyster, crab, and fish also may be given. Many tropical fish are meat-eaters, and some plant-eating fish can be trained to eat such food. Some “hard-to-keep” saltwater fishes need special food, such as sponges and live coral, but many types eat a variety of foods. Owners should feed only the amount that the fish will clean up promptly. Uneaten food drops to the bottom and rots, fouling the water and threatening the health of the fish.
A tropical fish aquarium should be covered with a flat pane of glass to control the temperature. This also keeps the fish from leaping out of the aquarium. Owners should grow water plants in the tank to keep the water in better condition and produce oxygen for the fish to breathe. Locate tanks away from bright sunlight, which also will control the temperature.

The most common tropical fish is the guppy. It comes from fresh waters of the Caribbean and South America. The female guppy grows about 2 inches (5 centimeters) long, and the male is even smaller. The female is gray, but the male is brilliantly rainbow-hued. Guppies breed at about 3 months of age and bear their young alive. Each female guppy produces from 20 to 50 young. See Guppy.
Other freshwater tropical fish that bear live young are the swordtail, platyfish, and black molly. Some tropical fish that bear their young in the egg stage are barbs, danios, rasboras, characins, and cichlids. The various labyrinth fishes are so named because they have a cavity with many branches in their head, usually above the gills. They store air in this cavity and use it as an accessory breathing organ. Some saltwater fish, such as clownfish and some damselfishes, can be bred and raised in home aquariums.