Turmeric << TUR muhr ihk >> is a plant that grows in southern Asia. Its fleshy roots are the source of a substance, also called turmeric, which is used mainly for dyeing. These roots are hard and tough. On the outside, they are brownish- or yellowish-green. When they are broken, they show a resinous interior that varies from orange-brown to deep reddish-brown. The roots are ready for the market after being cleaned, boiled for some hours, and then dried in an oven. The yellowish powder that they yield when ground has a strong, aromatic odor and a strong, pungent taste.
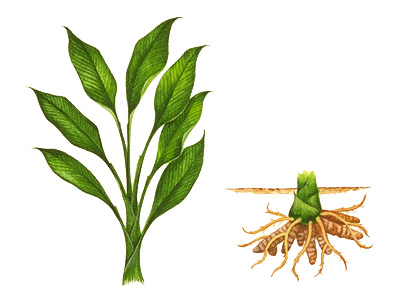
Turmeric has been used for hundreds of years as a dyestuff and as a spice. It is an important ingredient of curry powder and is used to color mustard (see Curry ). It does not yield a fast color, however, as a dyestuff. It can be used as a medicine for certain ailments, including inflammation and digestive issues. In India, people mix it with milk to make a tonic for overall wellbeing. Turmeric is useful in chemistry in making test papers for alkalies. With the addition of alkali, white paper soaked in a tincture of turmeric turns to reddish-brown and, on drying, to violet.
