Victorian Age, or Victorian Era, was a period of British history during the reign of Queen Victoria . Victoria reigned from 1837 to 1901. Victoria was a wise and capable monarch, and the United Kingdom reached the height of its power with her as queen. The United Kingdom built a great colonial empire overseas, and it achieved tremendous industrial expansion at home.
Victoria was born in 1819. Her uncle King William IV died in 1837 and had no heirs. As a result, Victoria succeeded to the throne. Just 18 years old, she relied on British Prime Minister Viscount Melbourne as a friend and adviser. Melbourne taught her about British politics and the constitution. His training did much to shape Victoria’s character as queen.

During her reign, Victoria accepted a reduction in the power of the monarchy and a shift from political to symbolic rule. British success during the Victorian Age was due largely to able prime ministers, including Melbourne, Sir Robert Peel , Viscount Palmerston , Benjamin Disraeli , William Gladstone , and the Marquess of Salisbury .
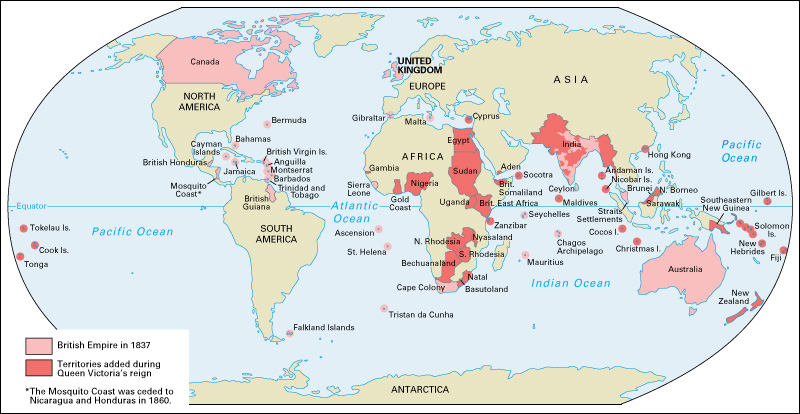
Europe was at peace for much of the Victorian Age. The period from the end of the Napoleonic Wars (1796-1815) to the start of World War I (1914-1918) is often called the Pax Britannica (Latin for British Peace). Nonetheless, the United Kingdom was involved in a number of smaller wars, mostly for colonial conquest. The British acquired the island of Hong Kong after fighting China in the First Anglo-Chinese War (1839-1842), also called the First Opium War. Strategic rivalries drew the United Kingdom into the Crimean War (1853-1856) against Russia . British troops also fought to protect interests in Africa , India , the Middle East , and Southeast Asia . The last major conflict of the Victorian Age was the Anglo-Boer War of 1899-1902, in what is now South Africa .
The United Kingdom established control of Egypt and many other areas during the Victorian Age. British colonies united in Australia and Canada , and these countries became important members of the British Empire . British industries benefited from the expanding empire, and the United Kingdom became the richest country in the world. The colonies were both sources of raw materials and markets for British manufactured goods.
During the Victorian Age, the United Kingdom changed from a mainly agricultural nation to a mainly industrial one. Its population increased by 50 percent. More people won the right to vote, and local government became more democratic. The British Parliament passed acts that improved labor conditions, required children to attend school, and reformed the civil service. In Ireland , which was part of the United Kingdom at that time, the Protestant Church of Ireland was separated from the government, and the land system was reformed.
Science, technology, and literature made great advances during the Victorian Age. Canals and railroads crisscrossed the country. The start of telegraph and, later, telephone service revolutionized the speed of long-distance communications. The British naturalist Charles Darwin became famous for his theories of evolution . Great novelists of the period included Charles Dickens , William Makepeace Thackeray , the Brontë sisters , and George Eliot (the pen name of Mary Ann Evans). Famous poets included Matthew Arnold , Robert Browning , Gerard Manley Hopkins , and Lord Tennyson . Oscar Wilde was a well-known author and playwright.
The Victorian Age ended with Victoria’s death in 1901. Her eldest son succeeded her as King Edward VII .
See also United Kingdom, History of the .
