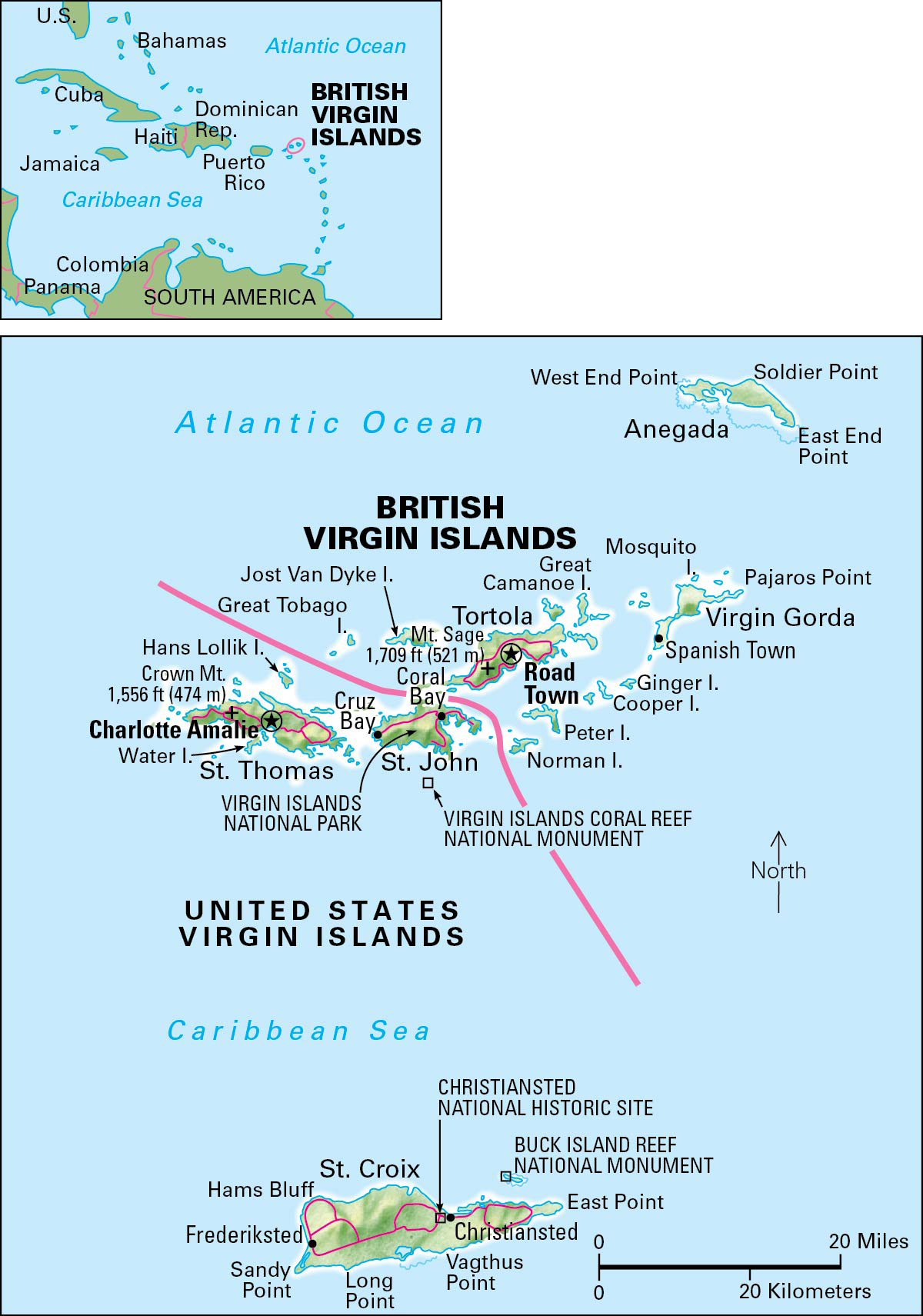
Virgin Islands, British, are an overseas territory of the United Kingdom in the Caribbean region. They lie near the western end of the Lesser Antilles island group. A channel called the Narrows separates them from the United States Virgin Islands. The territory has a land area of 58 square miles (151 square kilometers). It consists of 16 inhabited islands and more than 40 uninhabited islands and cays (reefs). The largest populated islands are Anegada, Jost Van Dyke, Tortola, and Virgin Gorda. Road Town (pop. 15,000), on Tortola, is the capital.
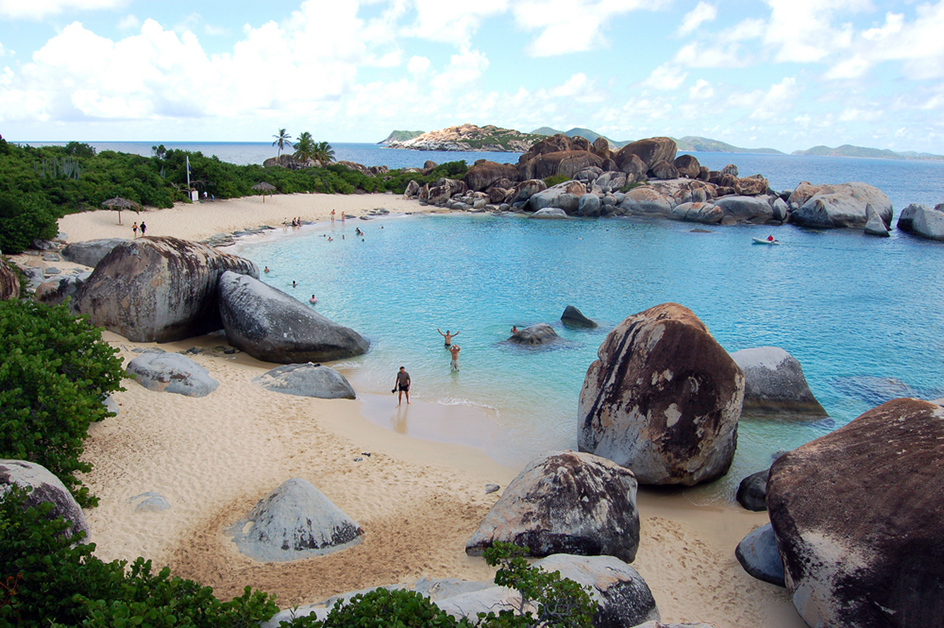

The islands have a subtropical climate. Trade winds blow for most of the year. Temperatures range from 70 to 90 °F (21 to 32 °C). The islands receive about 59 inches (130 centimeters) of rainfall annually. Mount Sage, on Tortola, is the islands’ highest point. It rises 1,709 feet (521 meters).
About 35,000 people live on the islands. About 75 percent are of African descent. The rest are of Asian, European, or mixed ancestry. English is the official language.
Tourism generates much of the territory’s income. Other major economic activities on the British Virgin Islands include construction, the distillation of rum, and offshore financial services.
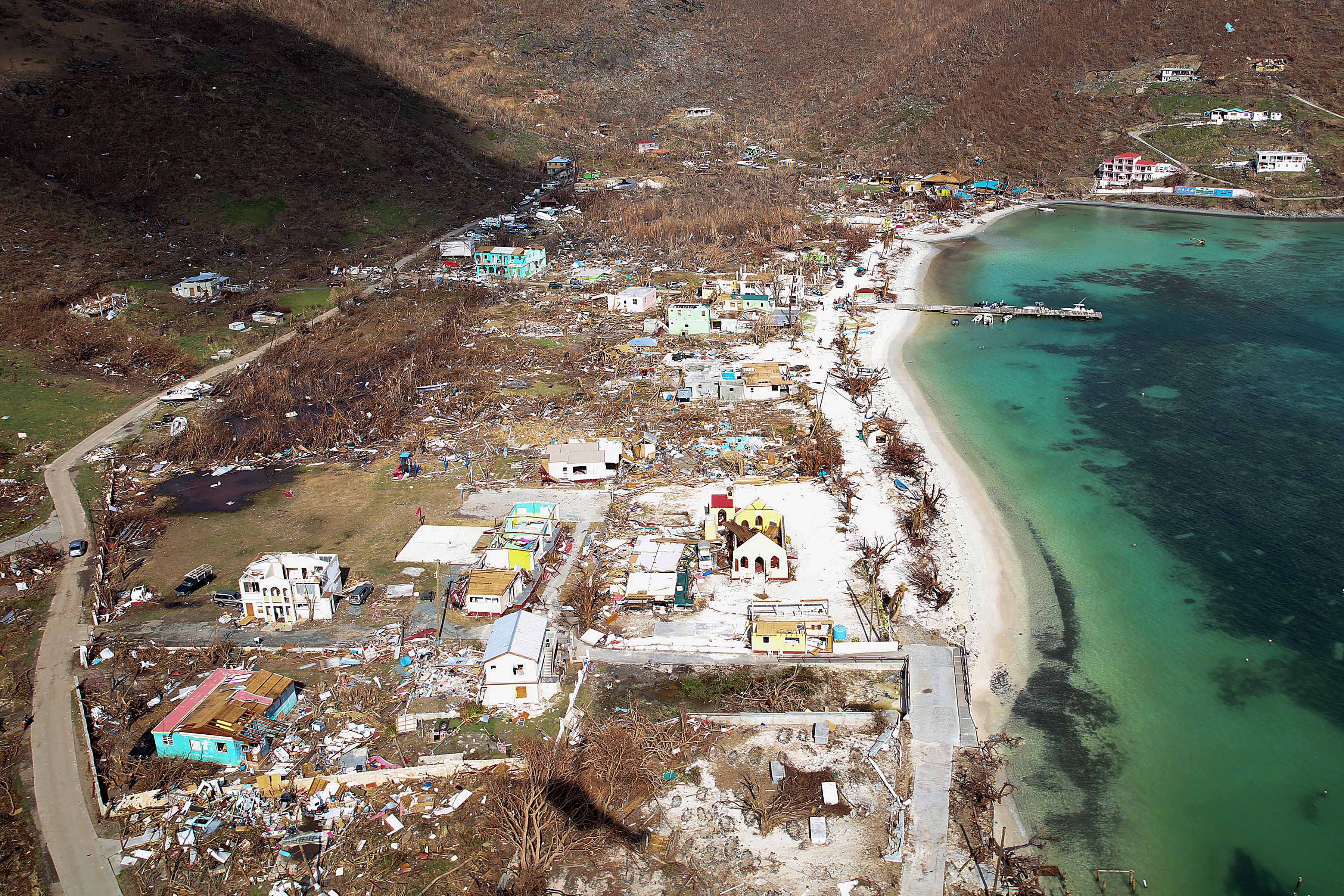
The Dutch settled on Tortola, in what are now called the British Virgin Islands, in 1648. England annexed the islands in 1672. In 2017, Hurricane Irma destroyed parts of the British Virgin Islands, killing four people and causing widespread damage.

See also British West Indies ; Caribbean Islands .
