Website is a collection of information on the World Wide Web, a system of computer files linked to one another on the internet. In addition to text, many websites contain pictures, sounds, and videos. People can view and use websites with a computer program called a web browser.
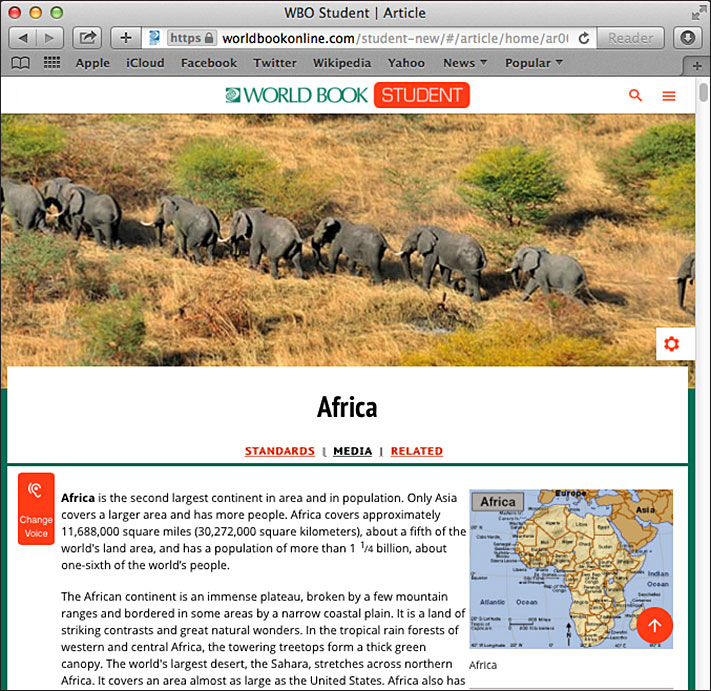
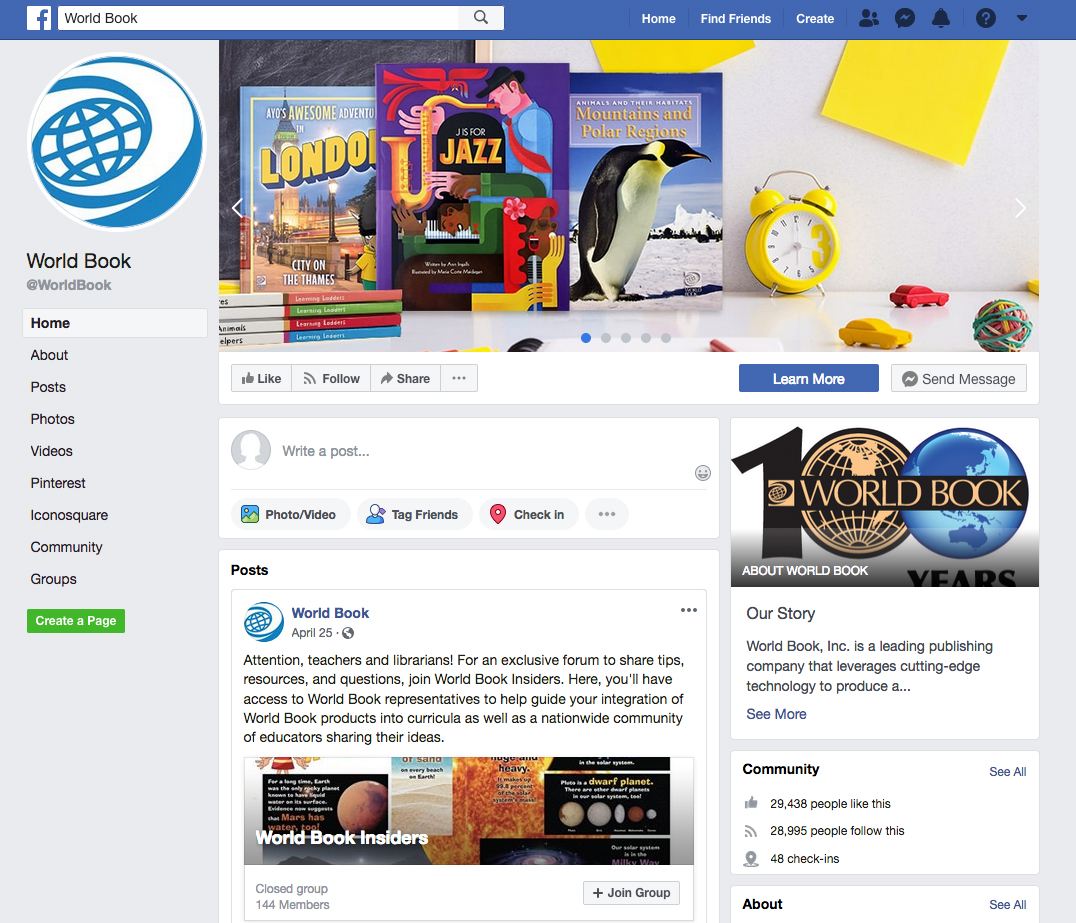
Many businesses, schools, government and nonprofit groups, and individuals have websites. The information on a website is arranged in separate displays called pages. A website can have hundreds or even thousands of pages. A starting page, called the home page, often resembles a table of contents of the information and features available on the site.
A website can be devoted to a single topic or can include a variety of topics, each spanning many pages. Some sites, such as social networking websites, allow users to create their own pages. Websites may also let users write and send emails, create documents and spreadsheets, and play games.
Websites and pages are created using a simple programming language called HyperText Markup Language (HTML). HTML controls how web pages appear in a user’s web browser. HTML also enables users to move directly from one page to another with hypertext links. Such links are typically highlighted words, phrases, or pictures related to a separate page. When a user clicks on a link, the browser displays the new page.
Websites are typically organized around a unique domain name. For example, the World Book website’s domain name is “worldbook.” A domain name works somewhat like a street name. Each page on a website has its own address, known as a uniform resource locator (URL), that contains the domain name. The URL indicates where on the internet a web page can be found, much like a specific house’s street address. For example, the URL for World Book’s home page is https://www.worldbook.com.
For other people to access a website, a site’s domain name must be registered. A nonprofit organization called the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) coordinates domain name registration. Registering a domain name typically requires a small annual fee. Anyone can register a domain name, so long as it is not already in use.
In addition to a registered domain name, websites require space to store their pages. Each web page is a computer file. Storing and providing access to these files typically requires a powerful computer called a server. A number of companies sell space on their servers for hosting other people’s websites. Many organizations and individuals own and operate their own servers.
