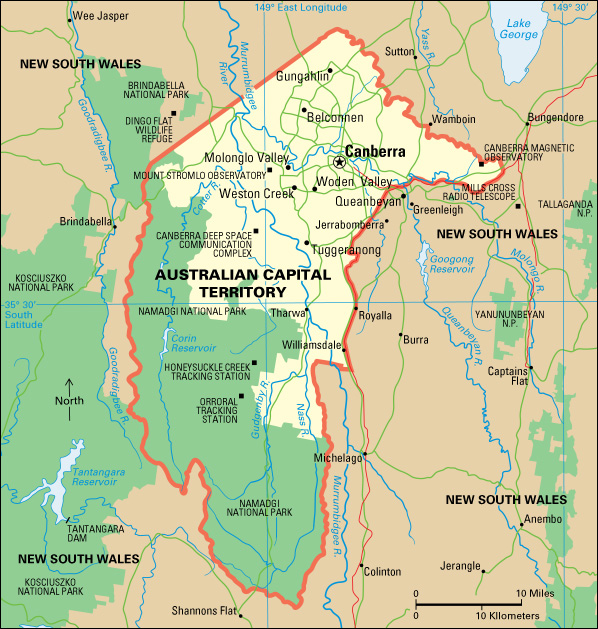
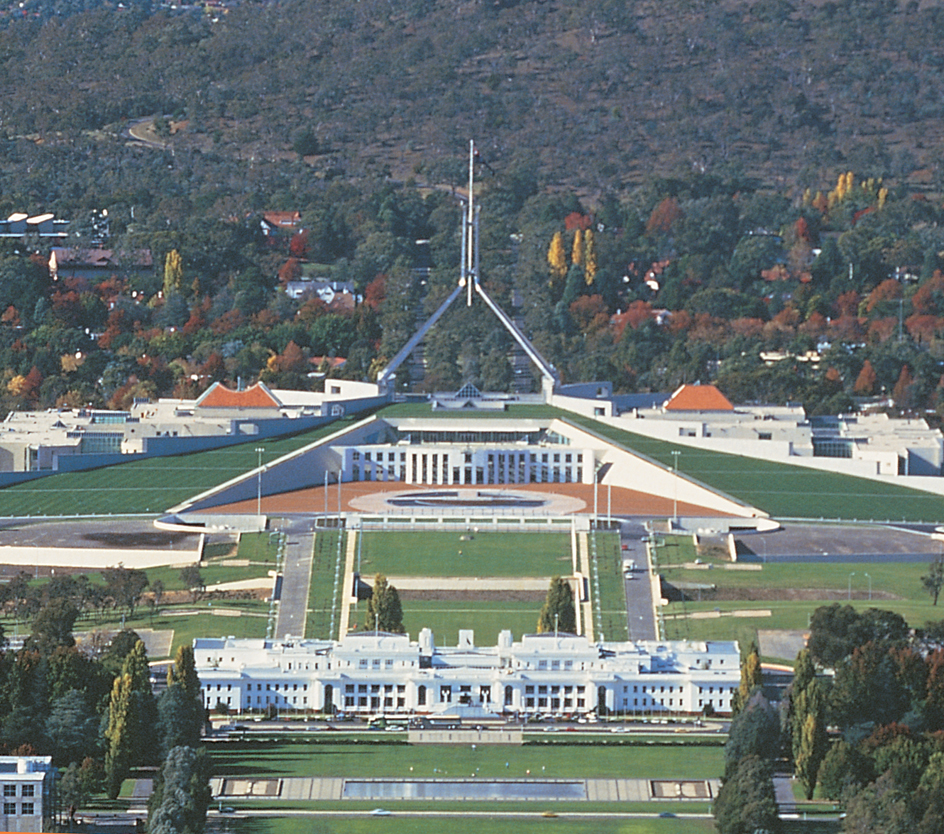
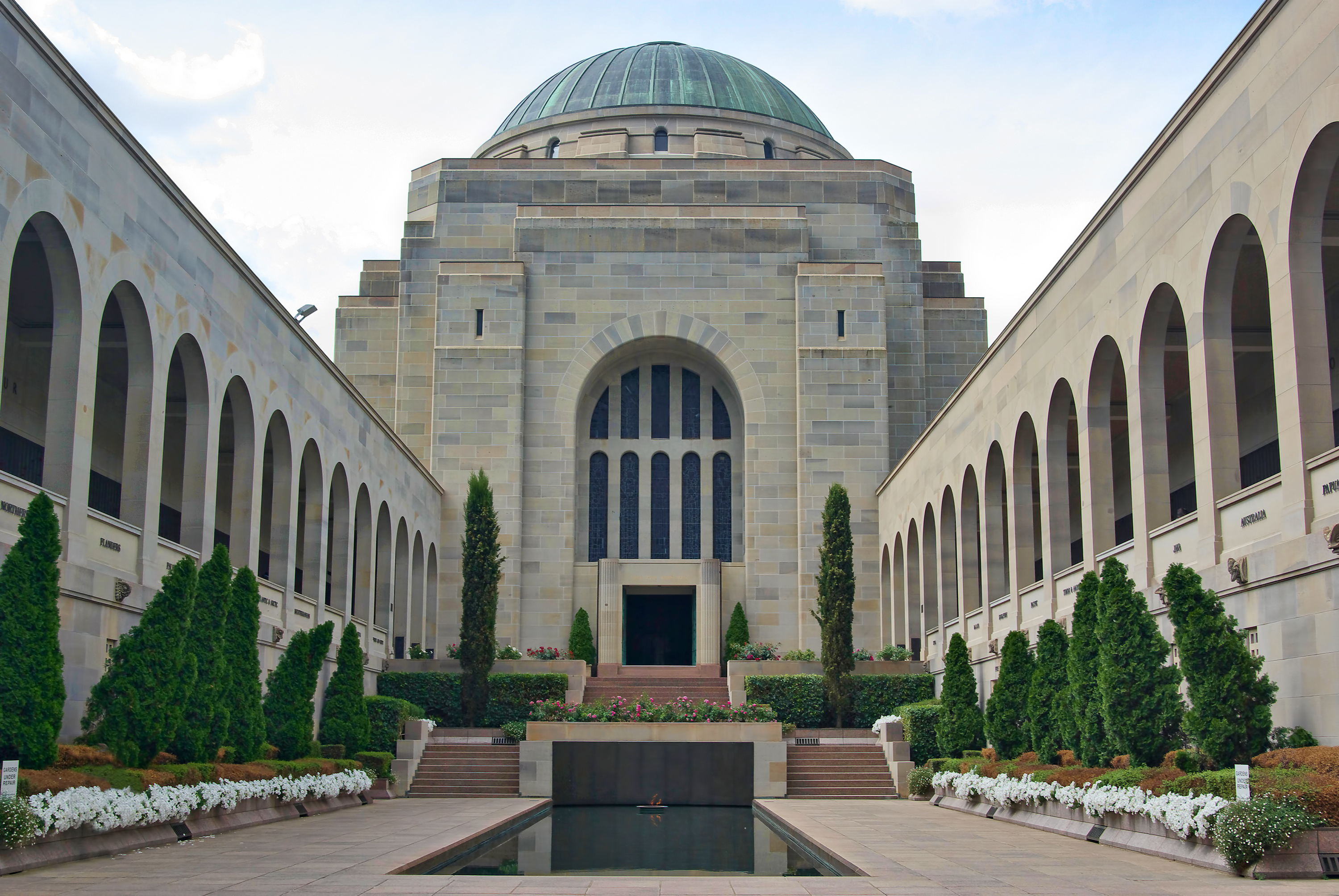
Australian Capital Territory (ACT) is the site of Canberra, Australia’s national capital. The ACT covers 910 square miles (2,358 square kilometers). It includes the urban area of Canberra as well as a national park, recreation areas, and historic and scenic sites. The 2021 Australian census reported that the ACT had 454,499 people.
The average rainfall in Canberra is about 36 inches (91 centimeters) a year. The average temperature is 69 °F (21 °C) in January and 42 °F (6 °C) in July.

Aboriginal peoples, the earliest inhabitants of Australia, lived in the ACT area at least 21,000 years ago. In 1820, British explorers became the first Europeans to reach the area. The British Parliament approved the Commonwealth of Australia Constitution Act in 1900. This act established the Commonwealth of Australia and provided for a federal seat of government with a territory of its own. In 1909, Charles R. Scrivener, a New South Wales district surveyor, recommended the present site of Canberra.
On Jan. 1, 1911, the Australian Capital Territory (called the Federal Capital Territory at first) was established. Construction of the capital began in 1913. In 1915, the Jervis Bay Territory was created on the New South Wales coast and was added to the ACT for use as a port. The Australian Parliament met in Canberra for the first time in 1927, and some government agencies began to be transferred there from Melbourne. In 1938 the Federal Capital Territory was officially renamed the Australian Capital Territory.
In 1989, the Australian Capital Territory gained powers of self-government similar to those in the Australian states. Voters in the territory elect a parliament called the Legislative Assembly. The Jervis Bay Territory ceased to be governed as part of the ACT after the ACT gained self-government.
In 2003, bushfires caused great damage in Canberra. In early January, lightning strikes started several bushfires in the Australian Alps west of the ACT. Severe weather conditions on January 18 caused the fires to advance rapidly, spreading through Namadgi National Park and into Canberra’s suburbs. The fires caused four deaths and destroyed about 500 houses in the ACT.
The city was again impacted by bushfires in late 2019 and early 2020, when fires blazing across large parts of eastern Australia made the air in many cities, including Canberra, dangerous to breathe. A bushfire that began in late January 2020 burned about 80 percent of the Namadgi National Park and part of the neighboring Tidbinbilla Nature Reserve.
In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic (worldwide epidemic) spread to Australia. The nation’s federal, state, and territorial governments took action to try to limit the spread of the disease and to ease the financial hardships caused by it.




See also Canberra; Duntroon; Snowy Mountains Scheme.
