Bariatric surgery is a medical procedure performed to produce weight loss for people who are severely obese. Many such individuals are 80 to 100 pounds (36 to 45 kilograms) or more above a healthy body weight. Bariatric surgery can produce loss of between 50 percent and 65 percent of excess body weight within one to two years. This reduction in weight often leads to an overall improvement in health and a better lifestyle, body image, and sense of well-being for the patient.
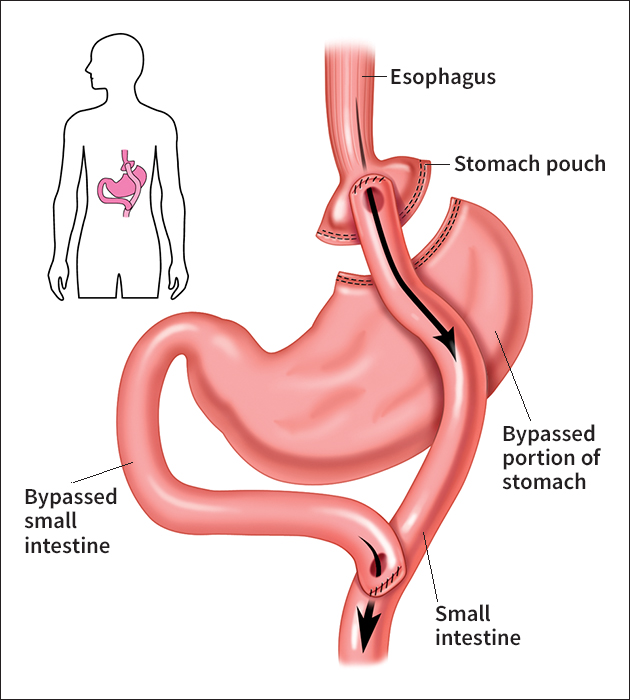
Bariatric operations can be restrictive, malabsorptive, or a combination of both. Restrictive procedures reduce stomach capacity so that people can eat only small amounts before feeling full. In one such operation, called gastric bypass, surgeons divide the stomach, producing a small pouch that can hold only about 1 ounce (30 milliliters) of food. They connect the pouch to the intestines, bypassing the lower stomach and part of the small intestine. In another operation, called adjustable gastric banding or lap-band surgery, surgeons place a silicone ring around the top portion of the stomach, making a small pouch. The ring can be inflated to decrease the opening where food passes into the lower stomach, limiting intake.
In malabsorptive procedures, surgeons reduce the length of the small intestine so that digestive juices do not mix with food until just before it reaches the large intestine. As a result, the digestive system digests food poorly and absorbs fewer calories and less fat and protein than normal, resulting in weight loss. Other procedures combine restrictive and malabsorptive elements. In these operations, surgeons typically divide the stomach and reduce the length of the small intestine available to digest food.
Risks from bariatric surgery include infection, bleeding, leakage of stomach contents, intestinal blockage, hernias, malnutrition, vitamin deficiencies, and blood clots. Serious complications are rare but can be fatal. Patients who undergo bariatric surgery must also adjust to a new lifestyle that includes careful diet control and regular exercise to maintain weight loss.
See also Body image ; Obesity ; Weight control (Surgery) .
