Pegasus << PEHG uh suhs >> is a constellation named for a winged horse in Greek mythology. Pegasus lies in the northern sky between the constellations Aquarius and Andromeda. It is best viewed around September through November. Pegasus was among the 48 constellations described by the ancient Greek mathematician Ptolemy. Today, it is one of 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union, the leading authority in the naming of heavenly objects.
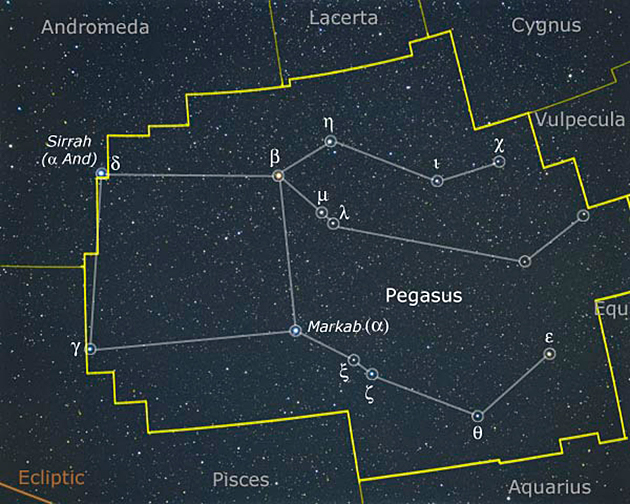
As commonly drawn, the constellation Pegasus includes about 13 to 15 main stars. A square of four stars marks the horse’s body or wing. A line and an arc of stars extend from one corner. They can be taken to represent the horse’s two front legs. An arc of four stars from an adjacent corner marks the head and neck.
In 1995, scientists discovered, in Pegasus, the first planet known to orbit a star similar to the sun. The planet orbits the star 51 Pegasi.
