Neogene Period, << NEE uh jeen, >> was a time in Earth’s history that lasted from about 23 million to 2.6 million years ago. It makes up the second part of the Cenozoic Era. The years of the Neogene Period were previously considered part of the Tertiary Period. But many scientific authorities no longer acknowledge the Tertiary Period.
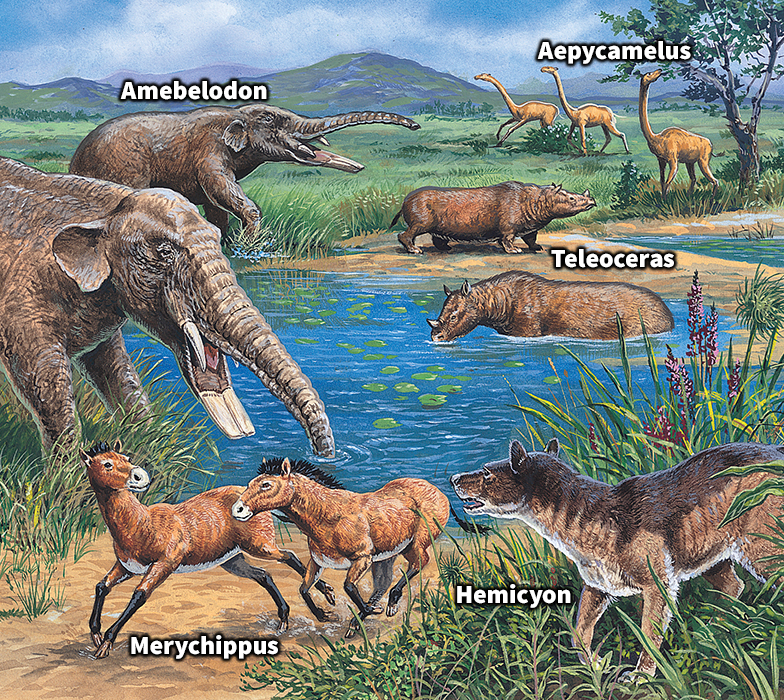
Mammals reached the peak of their diversity during the Neogene Period. For example, a large variety of apes appeared in Africa and Asia. Earth’s climate eventually became cooler and drier. Sea levels fell as the ice cap in Antarctica continued to grow. The continents had nearly reached their present arrangement.
The Neogene Period consisted of two shorter periods called epochs. They are the Miocene Epoch and the Pliocene Epoch.
The Miocene Epoch
lasted from about 23 million to 5.3 million years ago. About 6 million years ago, the collision of Africa and Europe completely closed off what is now the Mediterranean Sea. This area became a desert basin. Many scientists think it went through several cycles of drying and flooding during this time. Eventually, massive flooding from the Atlantic Ocean created the Mediterranean Sea.
The Pliocene Epoch
lasted from about 5.3 million to 2.6 million years ago. About 3 to 4 million years ago, the Isthmus of Panama formed as North and South America collided. An isthmus is a narrow strip of land. The formation of the isthmus separated the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. The isthmus also enabled land animals to pass between North and South America. At the end of the Pliocene, a series of ice ages began.
