James Webb Space Telescope, abbreviated as JWST or Webb, is the most powerful space observatory ever built. Webb was designed to replace some capabilities of the Hubble Space Telescope. With a main mirror that is 6.5 meters (21 feet) across, Webb has about seven times more light-collecting area than Hubble. But Webb is designed to study infrared light, a type of light with longer wavelengths than those of visible light. Thus, Webb does not replace Hubble’s visible-light capabilities.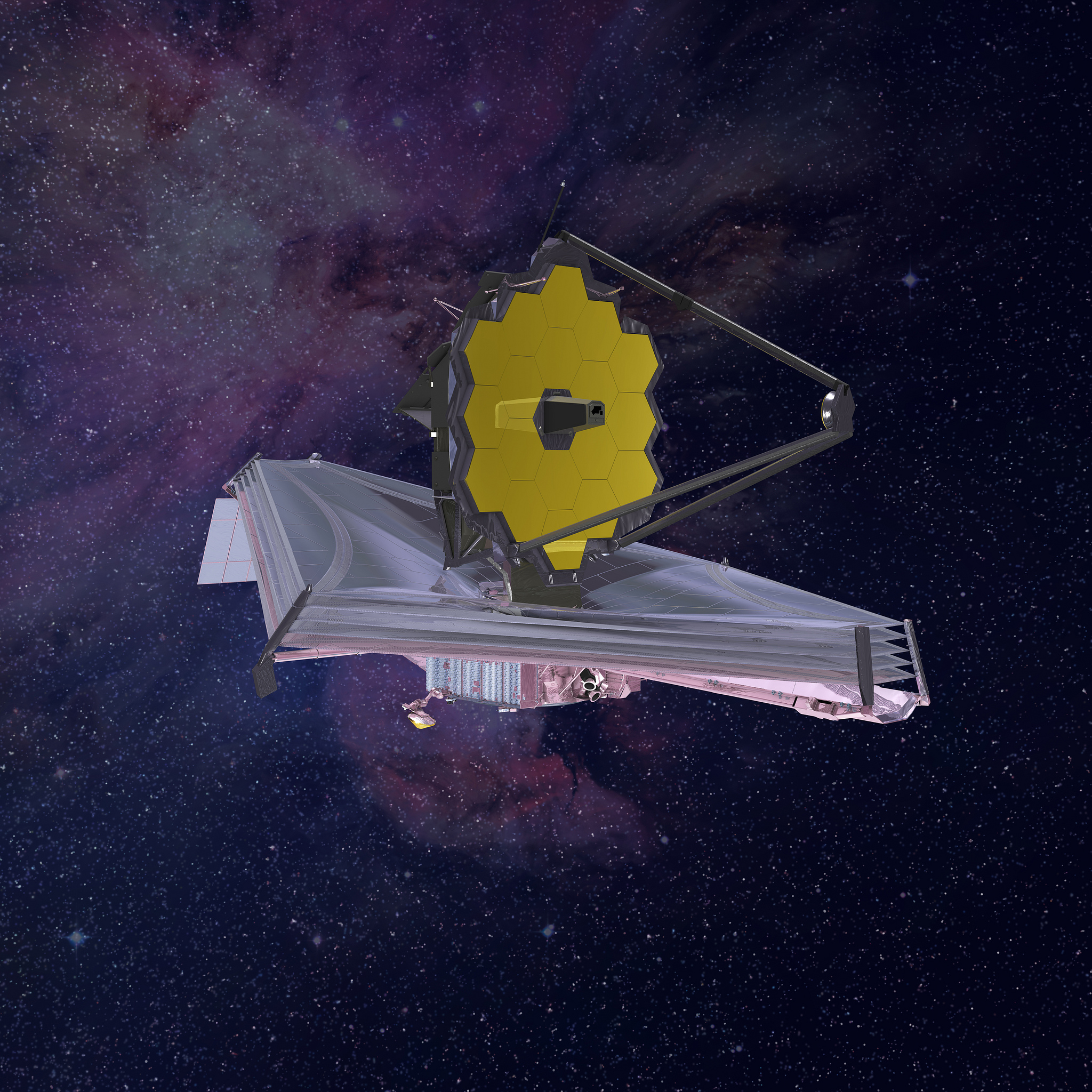 
Webb is a collaboration between the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). The Space Telescope Science Institute, which operates Hubble, manages Webb’s science operations. The Webb telescope is named after James Webb, the former NASA administrator who conceived and directed the Apollo program for most of the 1960’s.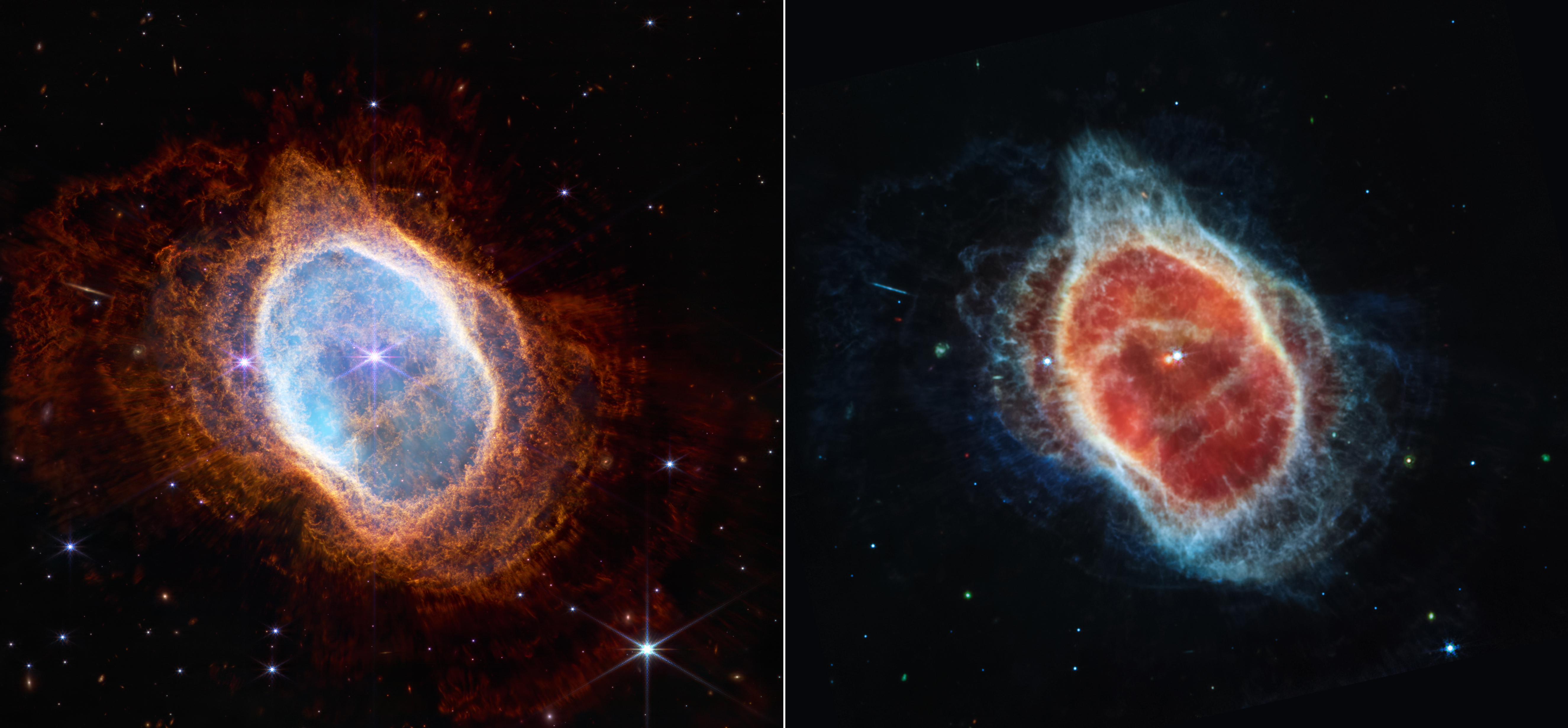 
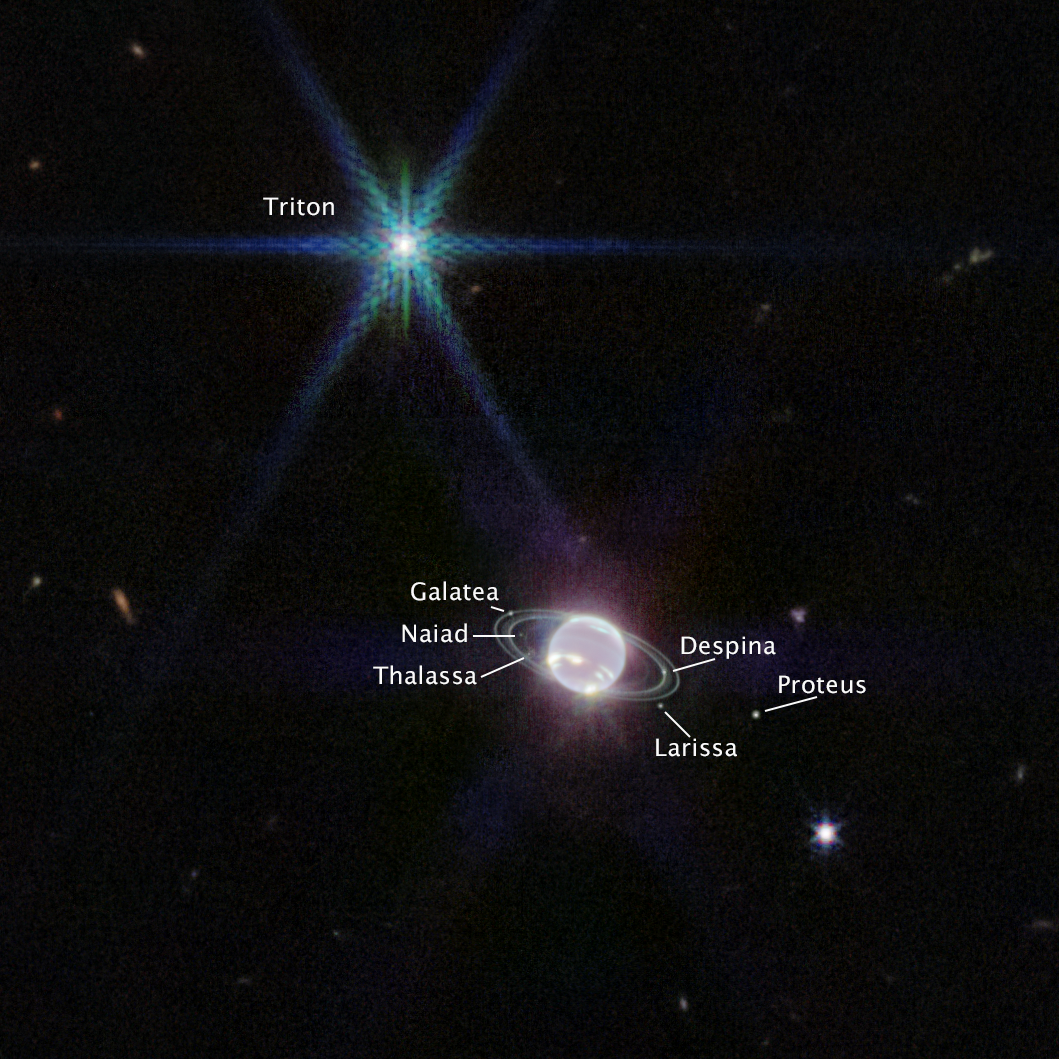
The Webb telescope enables scientists to study the history of the universe, nearly all the way back to a cosmic explosion called the big bang. It collects information on the first stars and galaxies that formed after the big bang, on the formation of planetary systems, and on the evolution of planets within the solar system.
Two of Webb’s four science instruments are specialized cameras. The third piece of equipment is a spectrometer, an instrument that spreads out light into a band of wavelengths called a spectrum. Astronomers can study such a spectrum for signs of light given off by certain molecules or atoms. The fourth piece of equipment contains both a specialized camera and a spectrometer.
Scientists and engineers built Webb with many innovative technologies. These include a primary (main) mirror made of many segments, which was folded up to fit in the launch rocket. After Webb reached space, the mirror segments unfolded, and scientists remotely adjusted the mirror to its proper shape. Other advanced features include specialized sensors that can record extremely weak light from faint objects. A large sun shield, about the size of a tennis court, prevents the infrared light from the sun, and the reflected sunlight from Earth and the moon, from interfering with observations. Infrared light is detected as heat. As a result, heat from any source, including the telescope itself, could potentially interfere with the infrared sensors. Thus, in addition, the telescope can actively cool certain sensors down to –477 °F (–266 °C). This additional cooling is to ensure that the sensors will not be affected by any heat source.
The Webb telescope was launched into space atop an Ariane 5 rocket on Dec. 25, 2021. It began science operations in 2022. Webb orbits the sun at a Lagrange point, a special point in space where the gravitational pulls of the sun and Earth are in balance. Webb is positioned at the Lagrange point known as L2. Orbiting the sun at L2 ensures Webb’s view is not blocked by shadows from Earth or the moon, and keeps the telescope in constant communication with Earth.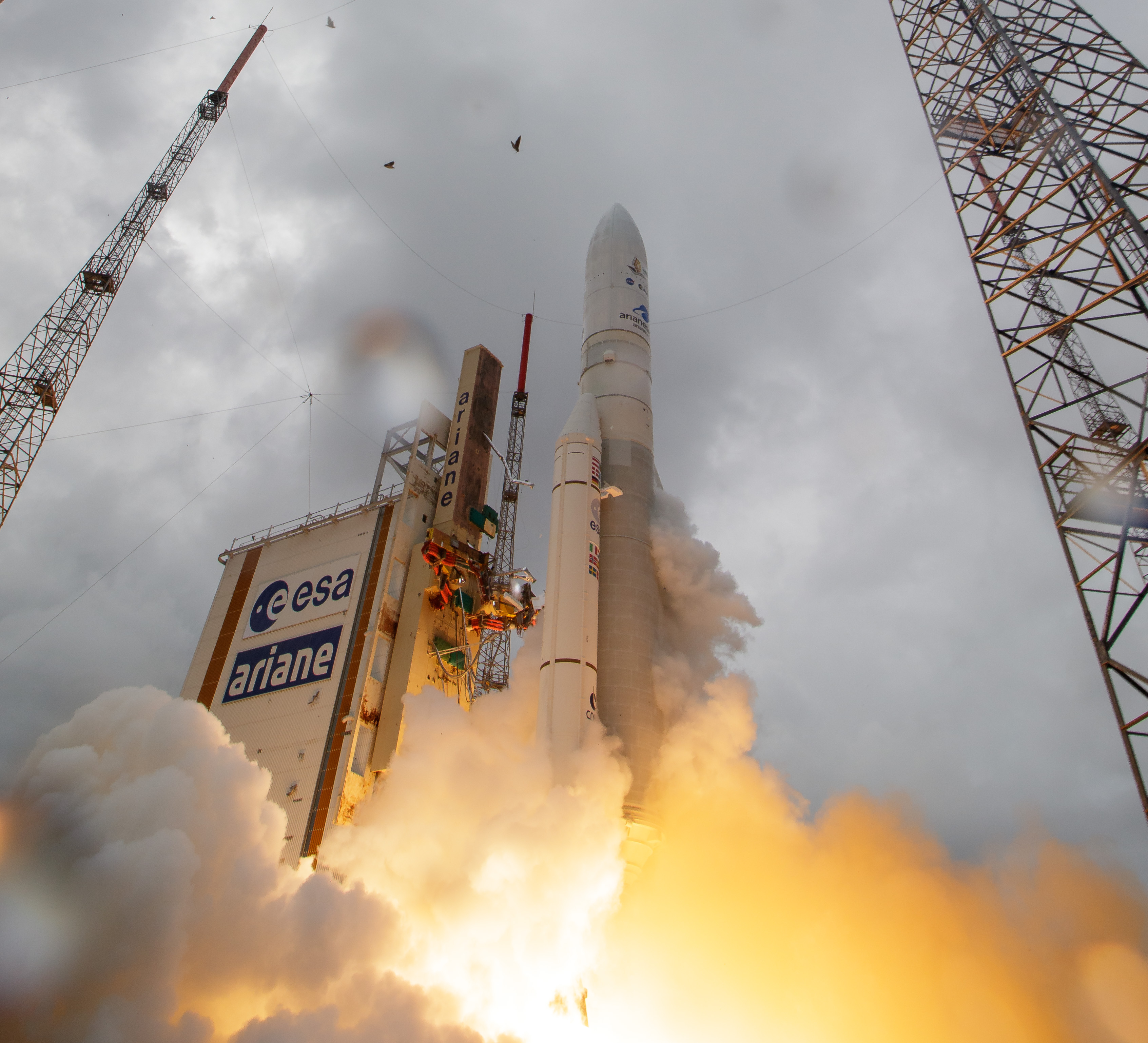 
See also Exoplanet; Mather, John Cromwell ; Observatory; Planet.
