Skeletal system is the collection of bones , joints , ligaments , and cartilage that provides a framework for the body. All vertebrates (animals with backbones), including humans, have a skeletal system. The skeletal system is one of the body’s major organ systems. It gives the body shape, protects vital organs, and provides a system of levers—operated by muscles —that enable the body to move.
Tissues.
Several specialized tissues make up the parts of the skeletal system. They include (1) bones, (2) cartilage, and (3) ligaments.
Bones
are located throughout the skeletal system where strength and stability are needed. Bones provide rigid structure for the body. They also contain bone marrow , the tissues that form blood . In addition, bones store such essential minerals as calcium, iron, magnesium, and phosphorus.
Cartilage
is a bluish-white rubbery tissue found at the ends of long bones and between the vertebrae (bones of the spine ). Cartilage cushions bones against shock and prevents them from rubbing against one another. Cartilage is also located in certain places where flexibility is important, such as the tip of the nose and the outer ear . Some vertebrates, such as sharks , lack bones entirely and have skeletons made up primarily of cartilage.
Ligaments
are strong bands of fibrous tissue that fit bones together and hold them in place. Ligaments provide stability at joints. Examples of ligaments include the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and medial collateral ligament (MCL). These ligaments help stabilize the knee . Stretching and tearing of ligaments are common injuries of the skeletal system.
The skeleton.
The skeleton is divided into the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. In humans, the axial skeleton consists of 80 bones in the skull , thorax (chest), and vertebral column (spine). These bones form the central axis of the body and protect the brain , spinal cord, heart , and lungs . The skull consists of 22 bones that form the face and enclose the brain. The bones of the skull are held together by immoveable joints called sutures. The thorax is composed of twelve pairs of ribs and the sternum (breastbone), forming a protective cage around the heart and lungs. The vertebral column consists of 24 vertebrae plus the sacrum and the coccyx (tailbone) at the bottom of the spine. The vertebral column protects the spinal cord and connects the upper body with the lower body. The U-shaped hyoid bone in the throat and three small bones called auditory ossicles within each ear complete the axial skeleton.
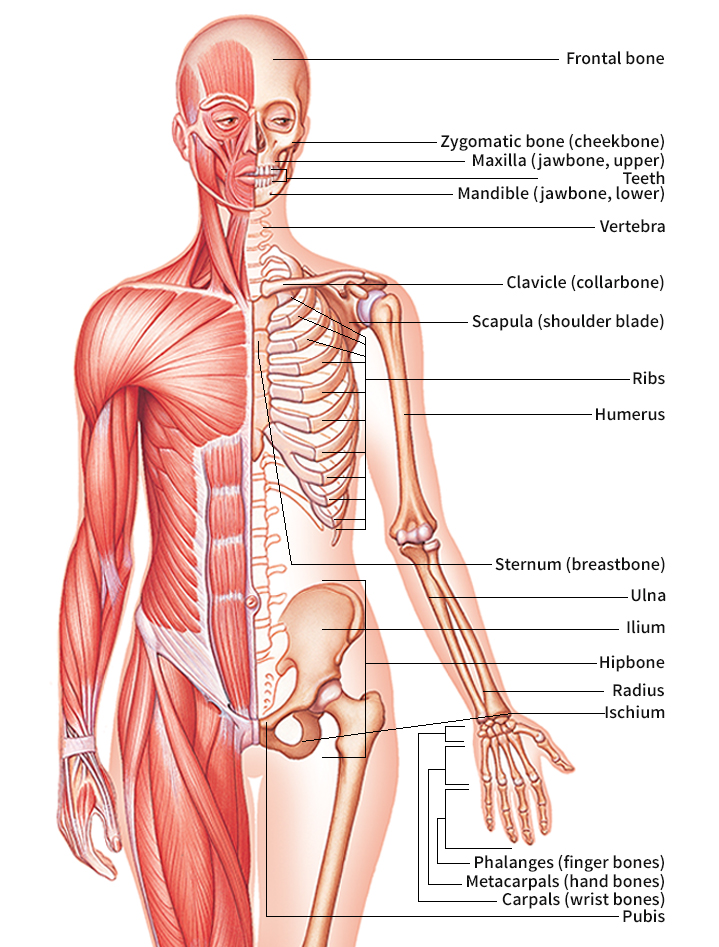
The appendicular skeleton in humans is formed by the 126 bones of the arms and legs . These bones enable the body to walk, run, and jump and to manipulate the environment by picking up and moving objects. The bones of the arm include the clavicle, scapula (shoulder blade), humerus, radius, ulna, and 27 bones of the hand . The bones of the leg are the hip bones, femur, tibia, fibula, and 26 bones of the foot .
Joints,
also called articulations, are points at which two or more bones or pieces of cartilage meet. All movements of the human skeleton occur at joints. Muscles are attached to the bones and cartilage of the skeletal system and generate the forces needed for joint movements.
